CHUẨN ĐOÁN VÀ SỬA CHỮA LỖI ABS FORD U3000 U3000:49 U3000:48
CHUẨN ĐOÁN VÀ SỬA CHỮA LỖI ABS FORD U3000 U3000:49 U3000:48
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – Diagnosis and Testing • 2012 Ford Focus
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – Diagnosis and Testing
| 206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control | 2012 – 2014 Focus |
| Diagnosis and Testing | Procedure revision date: 03/5/2013 |
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Chart
DTC Chart: Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) Module
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices.
REFER to: Diagnostic Methods (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) DTC Chart
| DTC | Description | Action |
| B10DF:46 | Master Cylinder Isolation Valve: Calibration/Parameter Memory Failure |
This DTC sets due to an internal failure of the ABS module or due to a calibration failure between the HCU and the ABS module. CLEAR the DTC and REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0001:01 | TCS Control Channel “A” Valve 1: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0002:01 | TCS Control Channel “A” Valve 2: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0003:01 | TCS Control Channel “B” Valve 1: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0004:01 | TCS Control Channel “B” Valve 2: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0010:01 | Left Front Inlet Control: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0011:01 | Left Front Outlet Control: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0014:01 | Right Front Inlet Control: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0015:01 | Right Front Outlet Control: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0018:01 | Left Rear Inlet Control: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0019:01 | Left Rear Outlet Control: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C001C:01 | Right Rear Inlet Control: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C001D:01 | Right Rear Outlet Control: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the ABS module has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0020:01 | ABS Pump Motor Control: General Electrical Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test H |
| C0020:1C | ABS Pump Motor Control: Circuit Voltage Out of Range |
GO to Pinpoint Test H |
| C0020:71 | ABS Pump Motor Control: Actuator Stuck |
GO to Pinpoint Test H |
| C0030:07 | Left Front Tone Wheel: Mechanical Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| C0031:07 | Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Mechanical Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| C0031:11 | Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Ground |
GO to Pinpoint Test O |
| C0031:15 | Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Battery or Open |
GO to Pinpoint Test O |
| C0031:4A | Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Incorrect Component Installed |
This DTC sets when the incorrect type of wheel speed sensor has been installed, bi-directional versus non-bi-directional. For information on wheel speed sensor types, REFER to: Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – System Operation and Component Description (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Description and Operation). VERIFY the correct wheel speed sensor has been installed (part number is stamped on the sensor). If the incorrect wheel speed sensor has been installed, INSTALL a new wheel speed sensor. REFER to: Front Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). CYCLE the ignition. DRIVE the vehicle and reach a speed of at least 20 km/h (12 mph) for the ABS module carry out a wheel speed sensor selftest. If the correct wheel speed sensor is installed, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0033:07 | Right Front Tone Wheel: Mechanical Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| C0034:07 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Mechanical Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| C0034:11 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Ground |
GO to Pinpoint Test O |
| C0034:15 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Battery or Open |
GO to Pinpoint Test O |
| C0034:4A | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Incorrect Component Installed |
This DTC sets when the incorrect type of wheel speed sensor has been installed, bi-directional versus non-bi-directional. For information on wheel speed sensor types, REFER to: Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – System Operation and Component Description (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Description and Operation). VERIFY the correct wheel speed sensor has been installed (part number is stamped on the sensor). If the incorrect wheel speed sensor has been installed, INSTALL a new wheel speed sensor. REFER to: Front Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). CYCLE the ignition. DRIVE the vehicle and reach a speed of at least 20 km/h (12 mph) for the ABS module carry out a wheel speed sensor selftest. If the correct wheel speed sensor is installed, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0036:07 | Left Rear Tone Wheel: Mechanical Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| C0037:07 | Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Mechanical Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| C0037:11 | Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Ground |
GO to Pinpoint Test P |
| C0037:15 | Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Battery or Open |
GO to Pinpoint Test P |
| C0037:4A | Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Incorrect Component Installed |
This DTC sets due to incomplete IVD initialization procedure or when the incorrect type of wheel speed sensor has been installed, bi-directional versus non-bi-directional. For information on wheel speed sensor types, REFER to: Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – System Operation and Component Description (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Description and Operation). If ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) U2300:51 or U2300:56 is also present, DIAGNOSE those Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) before diagnosing DTC C0037:4A. DIAGNOSE U2300:51 before diagnosing U2300:56. If ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) U2300:51 or U2300:56 are not present, VERIFY the correct wheel speed sensor has been installed (part number is stamped on the sensor). If the incorrect wheel speed sensor has been installed, INSTALL a new wheel speed sensor. REFER to: Rear Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). CYCLE the ignition. DRIVE the vehicle and reach a speed of at least 20 km/h (12 mph) for the ABS module carry out a wheel speed sensor selftest. If the correct wheel speed sensor is installed, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0039:07 | Right Rear Tone Wheel: Mechanical Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| C003A:07 | Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Mechanical Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test B |
| C003A:11 | Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Ground |
GO to Pinpoint Test P |
| C003A:15 | Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Battery or Open |
GO to Pinpoint Test P |
| C003A:4A | Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Incorrect Component Installed |
This DTC sets due to incomplete IVD initialization procedure or when the incorrect type of wheel speed sensor has been installed, bi-directional versus non-bi-directional. For information on wheel speed sensor types, REFER to: Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – System Operation and Component Description (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Description and Operation). If ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) U2300:51 or U2300:56 is also present, DIAGNOSE those Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) before diagnosing DTC C003A:4A. DIAGNOSE U2300:51 before diagnosing U2300:56. If ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) U2300:51 or U2300:56 are not present, VERIFY the correct wheel speed sensor has been installed (part number is stamped on the sensor). If the incorrect wheel speed sensor has been installed, INSTALL a new wheel speed sensor. REFER to: Rear Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). CYCLE the ignition. DRIVE the vehicle and reach a speed of at least 20 km/h (12 mph) for the ABS module carry out a wheel speed sensor selftest. If the correct wheel speed sensor is installed, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0040:64 | Brake Pedal Switch “A”: Signal Plausibility Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test C |
| C0040:87 | Brake Pedal Switch “A”: Missing Message |
GO to Pinpoint Test I |
| C0044:01 | Brake Pressure Sensor “A”: General Electrical Failure |
DIAGNOSE DTC C0040:64 before diagnosing this DTC. If DTC C0040:64 is not present, RECORD and then CLEAR all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). CYCLE the ignition from ON to OFF and back to ON. CARRY OUT the ABS module self-test. If this DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0044:28 | Brake Pressure Sensor “A”: Signal Bias Level Out of Range/Zero Adjustment Failure |
DIAGNOSE DTC C0040:64 before diagnosing this DTC. If Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) C0040:64 is not present, RECORD and CLEAR all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). CYCLE the ignition from ON to OFF and back to ON. CARRY OUT the IVD Initialization procedure, FOLLOW the diagnostic scan tool instructions. If the module fails the initialization procedure, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). If the module passes the initialization procedure, CARRY OUT the ABS module self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0044:54 | Brake Pressure Sensor “A”: Missing Calibration |
DIAGNOSE DTC C0040:64 before diagnosing this DTC. If Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) C0040:64 is not present, RECORD and CLEAR all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). CYCLE the ignition from ON to OFF and back to ON. CARRY OUT the IVD Initialization procedure, FOLLOW the diagnostic scan tool instructions. If the module fails the initialization procedure, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). If the module passes the initialization procedure, CARRY OUT the ABS module self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0044:64 | Brake Pressure Sensor “A”: Signal Plausibility Failure |
DIAGNOSE DTC C0040:64 before diagnosing this DTC. If DTC C0040:64 is not present, BLEED the brake system. REFER to: Brake System Bleeding (206-00 Brake System – General Information, General Procedures). CYCLE the ignition from ON to OFF and back to ON. CARRY OUT the ABS module self-test. If this DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0051:28 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Signal Bias Level Out of Range/Zero Adjustment Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test M |
| C0051:54 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Missing Calibration |
GO to Pinpoint Test M |
| C0061:28 | Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Signal Bias Level Out of Range/Zero Adjustment Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| C0061:2F | Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Signal Erratic |
GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| C0061:54 | Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Missing Calibration |
This DTC sets if the stability sensors in the RCM have not been calibrated or the calibration has been lost. CARRY OUT the IVD Initialization procedure, FOLLOW the diagnostic scan tool instructions. If the module fails the initialization procedure, VERIFY the RCM is installed correctly and that the fasteners are tightened to specifications. REINSTALL or INSTALL new as necessary. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). If the RCM is OK, CARRY OUT the RCM self-test. RETRIEVE and RECORD any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REFER to: Airbag Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) – Vehicles With: First and Second Row Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) With Driver Knee Airbag (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Diagnosis and Testing). If the module passes the initialization procedure, CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). CYCLE the ignition from ON to OFF and back to ON. CARRY OUT the ABS module self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0061:64 | Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Signal Plausibility Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| C0062:01 | Longitudinal Acceleration Sensor: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC sets if there is an internal failure of the stability sensor inside the RCM. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). CYCLE the ignition from ON to OFF and back to ON. CARRY OUT the ABS module self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new RCM. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). |
| C0062:28 | Longitudinal Acceleration Sensor: Signal Bias Level Out of Range/Zero Adjustment Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| C0062:4A | Longitudinal Acceleration Sensor: Incorrect Component Installed |
This DTC sets due to incomplete or improper Programmable Module Installation (PMI) procedures or when an incorrect RCM has been installed. CHECK vehicle service history for recent service actions related to the RCM. If there have been recent service actions with the RCM, REPEAT the Programmable Module Installation (PMI) procedure as directed by the diagnostic scan tool. If there have been no recent service actions related to the RCM, INSTALL a new RCM. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). Be sure to follow all diagnostic scan tool instructions as they relate to Programmable Module Installation (PMI). |
| C0062:54 | Longitudinal Acceleration Sensor: Missing Calibration |
This DTC sets if the stability sensors in the RCM have not been calibrated or the calibration has been lost. CARRY OUT the IVD Initialization procedure, FOLLOW the diagnostic scan tool instructions. If the module fails the initialization procedure, VERIFY the RCM is installed correctly and that the fasteners are tightened to specifications. REINSTALL or INSTALL new as necessary. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). If the RCM is OK, CARRY OUT the RCM self-test. RETRIEVE and RECORD any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REFER to: Airbag Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) – Vehicles With: First and Second Row Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) With Driver Knee Airbag (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Diagnosis and Testing). If the module passes the initialization procedure, CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). CYCLE the ignition from ON to OFF and back to ON. CARRY OUT the ABS module self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| C0062:64 | Longitudinal Acceleration Sensor: Signal Plausibility Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| C0062:76 | Longitudinal Acceleration Sensor: Wrong Mounting Position |
Due to the nature of the longitudinal acceleration sensor, the RCM must be installed in the correct orientation to the centerline of the vehicle. This DTC sets if the RCM has been installed in the wrong position. VERIFY the RCM is installed correctly and the fasteners are tightened to specifications. REINSTALL or INSTALL new as necessary. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). If the RCM is OK, CARRY OUT the RCM self-test. RETRIEVE and RECORD any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REFER to: Airbag Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) – Vehicles With: First and Second Row Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) With Driver Knee Airbag (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| C0063:01 | Yaw Rate Sensor: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC sets if there is an internal failure of the stability sensor inside the RCM. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). CYCLE the ignition from ON to OFF and back to ON. CARRY OUT the ABS module self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new RCM. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). |
| C0063:28 | Yaw Rate Sensor: Signal Bias Level Out of Range/Zero Adjustment Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| C0063:2F | Yaw Rate Sensor: Signal Erratic |
GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| C0063:64 | Yaw Rate Sensor: Signal Plausibility Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| C006B:00 | Stability System Active Too Long: No Sub Type Information |
This DTC is for informational purposes only and sets along with one or more stability sensor Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). RETRIEVE and DIAGNOSE all other ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). |
| C0072:68 | Brake Temperature Too High: Event Information |
This DTC sets when the temperature of the brake discs/drums, as calculated by the ABS module, exceeds a predetermined threshold, 450°C (841.4°F). This DTC usually sets due to the stability system being activated too long, excessive traction control events, excessive anti-lock events, etc. RETRIEVE and DIAGNOSE all other ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). |
| C1A41:64 | Clutch Pedal Sensor: Signal Plausibility Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test N |
| P1701:81 | Reverse Engagement Error: Invalid Serial Data Received |
This DTC sets when the ABS module receives invalid network data from the TCM (automatic transmission) or PCM (manual transmission). RETRIEVE and REPAIR all non-network Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in the TCM or PCM. For TCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), REFER to: Automatic Transmission (307-01 Automatic Transmission – Vehicles With: 6-Speed PowerShift Transmission – DPS6/6DCT250) . For PCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| U0001:88 | High Speed CAN Communication Bus: Bus Off |
The module could not communicate on the network at a point in time. The fault is not currently present since the module had to communicate with the diagnostic scan tool to report this DTC. VERIFY the integrity of the connectors and wiring. Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 14 for schematic and connector information. |
| U0028:55 | Vehicle Communication Bus “A”: Not Configured |
The ABS module and the RCM exchange and store identification information for future reference. This DTC sets due to incomplete or improper Programmable Module Installation (PMI) procedures. CHECK vehicle service history for recent service actions related to the RCM and ABS module. If there have been recent service actions with one or both of the modules, REPEAT the Programmable Module Installation (PMI) procedure as directed by the diagnostic scan tool. If there have been no recent service actions, INSTALL a new RCM to correct the failure to retain configuration data. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). |
| U0028:88 | Vehicle Communication Bus “A”: Bus Off |
GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| U0100:00 | Lost Communication With ECM/PCM “A”: No Sub Type Information |
GO to Pinpoint Test I |
| U0101:00 | Lost Communication With TCM: No Sub Type Information |
GO to Pinpoint Test J |
| U0126:00 | Lost Communication With Steering Angle Sensor Module: No Sub Type Information |
GO to Pinpoint Test K |
| U0140:00 | Lost Communication With Body Control Module: No Sub Type Information |
GO to Pinpoint Test D |
| U0151:00 | Lost Communication With Restraints Control Module: No Sub Type Information |
GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| U0300:00 | Internal Control Module Software Incompatibility: No Sub Type Information |
GO to Pinpoint Test R |
| U0300:51 | Internal Control Module Software Incompatibility: Not Programmed |
CHECK vehicle service history for recent service actions related to the ABS module. This DTC sets due to incomplete or improper flash programming procedures. If there have been recent service actions with the ABS module, REPEAT the programming procedure as directed by the diagnostic scan tool. If there have been no recent service actions, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| U0401:00 | Invalid Data Received From ECM/PCM “A”: No Sub Type Information |
This DTC sets when the ABS module receives invalid network data from the PCM. RETRIEVE and REPAIR all non-network Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in the PCM. REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| U0401:41 | Invalid Data Received From ECM/PCM “A”: General Checksum Failure |
This DTC sets when the ABS module receives invalid network data from the PCM. RETRIEVE and REPAIR all non-network Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in the PCM. REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| U0401:68 | Invalid Data Received From ECM/PCM “A”: Event Information |
This DTC sets when the ABS module receives invalid network data from the PCM. RETRIEVE and REPAIR all non-network Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in the PCM. REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| U0402:68 | Invalid Data Received From TCM: Event Information |
This DTC sets when the ABS module receives invalid network data from the TCM. RETRIEVE and REPAIR all non-network Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in the TCM. REFER to: Automatic Transmission (307-01 Automatic Transmission – Vehicles With: 6-Speed PowerShift Transmission – DPS6/6DCT250) . |
| U0428:00 | Invalid Data Received From Steering Angle Sensor Module: No Sub Type Information |
GO to Pinpoint Test M |
| U0428:2F | Invalid Data Received From Steering Angle Sensor Module: Signal Erratic |
This is an intermittent DTC that is stored only due to temporary disturbances of the signals received from the SASM. If DTC U0428:64 is also present, GO to Pinpoint Test M If this is the only ABS module DTC retrieved; CLEAR the DTC, TEST DRIVE the vehicle above 20 km/h (12 mph) and make at least 2 right turns and 2 left turns. If the DTC returns, GO to Pinpoint Test M If the DTC does not return, RELEASE the vehicle |
| U0428:41 | Invalid Data Received From Steering Angle Sensor Module: General Checksum Failure |
If DTC U0126:00 is also present, DIAGNOSE DTC U0126:00 first. This DTC sets when the ABS module receives invalid network data from the SASM. RETRIEVE and REPAIR all non-network Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in the SASM. |
| U0428:61 | Invalid Data Received From Steering Angle Sensor Module: Signal Calculation Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test M |
| U0428:62 | Invalid Data Received From Steering Angle Sensor Module: Signal Compare Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test M |
| U0428:64 | Invalid Data Received From Steering Angle Sensor Module: Signal Plausibility Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test M |
| U0428:68 | Invalid Data Received From Steering Angle Sensor Module: Event Information |
GO to Pinpoint Test M |
| U0452:41 | Invalid Data Received From Restraints Control Module: General Checksum Failure |
If DTC U0151:00 is also present, DIAGNOSE DTC U0151:00 first. This DTC sets when the ABS module receives invalid network data from the RCM. RETRIEVE and REPAIR all non-network Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in the RCM. REFER to: Airbag Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) – Vehicles With: First and Second Row Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) With Driver Knee Airbag (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Diagnosis and Testing). |

| U0452:4A | Invalid Data Received From Restraints Control Module: Incorrect Component Installed |
This DTC sets when the RCM installed in the vehicle is either the wrong module, has not been configured or has been configured incorrectly. CHECK vehicle service history for recent service actions related to the RCM. If there have been recent service actions with the RCM, REPEAT the Programmable Module Installation (PMI) procedure as directed by the diagnostic scan tool. If there have been no recent service actions, INSTALL a new RCM to correct the failure to retain configuration data. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). |
| U0452:86 | Invalid Data Received From Restraints Control Module: Signal Invalid |
GO to Pinpoint Test G |
| U1A14:00 | CAN Initialization Failure: No Sub Type Information |
CLEAR the DTC. CYCLE the ignition. CARRY OUT the ABS module selftest. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly to correct the failure to retain configuration data. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). If the DTC does not return, the condition to set the DTC is not present at this time. The cause may be intermittent. |
| U2007:46 | Valve(s): Calibration/Parameter Memory Failure |
This DTC sets due to an internal failure of the ABS module or due to a calibration failure between the HCU and the ABS module. CLEAR the DTC and REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| U2100:00 | Initial Configuration Not Complete: No Sub Type Information |
CHECK the service history for recent service actions related to the ABS module. This DTC sets due to incomplete IVD initialization procedure. If there have been recent service actions with this module, REPEAT the IVD initialization procedure as directed by the diagnostic scan tool. If there have been no recent service actions, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly to correct the failure to retain configuration data. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| U2101:00 | Control Module Configuration Incompatible: No Sub Type Information |
This DTC sets if the vehicle configuration information sent from the BCM does not match what is stored in the ABS module. DIAGNOSE all BCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and any ABS module lost communication or invalid data Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that are preset before diagnosing this DTC. If there are no BCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) or ABS module lost communication or invalid data Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present, CHECK vehicle service history for recent service actions related to the ABS module or BCM. This DTC sets due to incomplete or improper flash programming procedures. If there have been recent service actions with the ABS module or BCM, REPEAT the programming procedure as directed by the diagnostic scan tool. If there have been no recent service actions, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly to correct the failure to retain configuration data. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| U2300:51 | Central Configuration: Not Programmed |
CHECK the service history for recent service actions related to the ABS module. This DTC sets due to incomplete IVD initialization procedure. If there have been recent service actions with this module, CARRY OUT the IVD Initialization procedure, FOLLOW the diagnostic scan tool instructions. If there have been no recent service actions, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly to correct the failure to retain configuration data. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| U2300:54 | Central Configuration: Missing Calibration |
This DTC sets when the ABS module has not received the vehicle configuration from the BCM. If ABS module DTC U0140:00 is also present, DIAGNOSE U0140:00 before diagnosing DTC U2300:54. If DTC U0140:00 is not present, RETRIEVE and DIAGNOSE all BCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). If the BCM does not communicate with the diagnostic scan tool, REFER to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Diagnosis and Testing). If there are no Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the BCM, then the BCM or ABS module could not communicate on the network at a point in time. The fault is not currently present since the ABS module had to communicate with the diagnostic scan tool to report this DTC. VERIFY the integrity of the connectors and wiring. Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 14 for schematic and connector information. |
| U2300:55 | Central Configuration: Not Configured |
CHECK the service history for recent service actions related to the ABS module. This DTC sets due to incomplete IVD initialization procedure. If there have been recent service actions with this module, CARRY OUT the IVD inialization procedure, FOLLOW the diagnostic scan tool instructions. If there have been no recent service actions, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly to correct the failure to retain configuration data. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| U2300:56 | Central Configuration: Invalid / Incompatible Configuration |
CHECK the service history for recent service actions related to the ABS module and BCM. This DTC sets due to incomplete IVD initialization procedure. If there have been recent service actions with the ABS module or BCM, REPEAT the IVD initialization procedure as directed by the diagnostic scan tool. If there have been no recent service actions, INSTALL a new BCM to correct the failure to retain software data. REFER to: Body Control Module (BCM) (419-10 Multifunction Electronic Modules, Removal and Installation). |
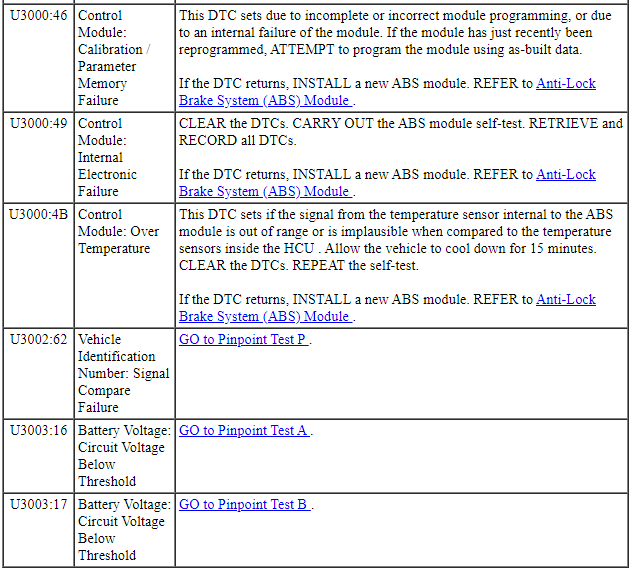
| U3000:48 | Control Module: Supervision Software Failure |
CLEAR the DTC. CYCLE the ignition. CARRY OUT the ABS module selftest. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly to correct the failure to retain configuration data. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). If the DTC does not return, the condition to set the DTC is not present at this time. The cause may be intermittent. |
| U3000:49 | Control Module: Internal Electronic Failure |
CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). CARRY OUT the ABS module self-test. RETRIEVE and RECORD all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). If the DTC returns INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU assembly. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| U3003:08 | Battery Voltage: Bus Signal / Message Failure |
This DTC sets when the High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) network is shorted together, shorted to ground, shorted to voltage or open. If DTC U3003:16 is also present, DIAGNOSE DTC U3003:16 before diagnosing DTC U3003:08. If DTC U3003:16 is not present, DIAGNOSE the communication network. REFER to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| U3003:16 | Battery Voltage: Circuit Voltage Below Threshold |
GO to Pinpoint Test A |
| U3003:17 | Battery Voltage: Circuit Voltage Above Threshold |
GO to Pinpoint Test F |
| U3003:62 | Battery Voltage: Signal Compare Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test Q |
DTC Chart: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM)
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices.
REFER to: Diagnostic Methods (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) DTC Chart
| C1B00:49 | Steering Angle Sensor: Internal Electrical Failure |
CHECK vehicle service history for recent service actions related to the SASM. This DTC sets due to incomplete or improper flash programming procedures. If there have been recent service actions with the SASM, REPEAT the programming procedure as directed by the diagnostic scan tool. If there have been no recent service actions, CLEAR the DTC, CYCLE the ignition, CARRY OUT the SASM self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new SASM to correct the failure to retain software data. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). |
| C1B00:61 | Steering Angle Sensor: Signal Calculation Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the SASM has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
| C1B00:62 | Steering Angle Sensor: Signal Compare Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the SASM has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
| C1B00:64 | Steering Angle Sensor: Signal Plausibility Failure |
CLEAR the DTC. TEST DRIVE the vehicle and CARRY OUT at least 1 left turn and 1 right turn. CARRY OUT a SASM self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
| C1B00:81 | Steering Angle Sensor: Invalid Serial Data Received |
This DTC indicates that part of the SASM has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
| C1B00:85 | Steering Angle Sensor: Signal Above Allowable Range |
SET the front wheels to the straight ahead position. Using a diagnostic scan tool, OBSERVE the SASM steering wheel angle (SW_ANGLE) Parameter Identification (PID). If the Parameter Identification (PID) displays 0 degrees, CLEAR the DTC, REPEAT the SASM self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). If the Parameter Identification (PID) displays more than 360 degrees, SET the ignition to OFF. REMOVE the SASM, REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). Leave the electrical connector connected. SET the ignition to ON (this causes Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) to set in multiple modules). Manually ADJUST the SASM until the SW_ANGLE Parameter Identification (PID) displays 0 degrees. SET the ignition to OFF. INSTALL the SASM. CLEAR all Continuous Memory Diagnostic Trouble Codes (CMDTCs) in all modules. |
| C1B00:87 | Steering Angle Sensor: Missing Message |
REFER to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| C1B00:92 | Steering Angle Sensor: Performance or Incorrect Operation |
CLEAR the DTC. TEST DRIVE the vehicle and CARRY OUT at least 1 left turn and 1 right turn. CARRY OUT a SASM self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
| C1B00:96 | Steering Angle Sensor: Component Internal Failure |
This DTC indicates that part of the SASM has failed internally. CLEAR the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REPEAT the self-test. If the DTC returns, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
| U0001:88 | High Speed CAN Communication Bus: Bus Off |
The module could not communicate on the network at a point in time. The fault is not currently present since the module had to communicate with the diagnostic scan tool to report this DTC. VERIFY the integrity of the connectors and wiring. Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 14 for schematic and connector information. |
| U0140:00 | Lost Communication With Body Control Module: No Sub Type Information |
GO to Pinpoint Test D |
| U0300:00 | Internal Control Module Software Incompatibility: No Sub Type Information |
GO to Pinpoint Test R |
| U3003:62 | Battery Voltage: Signal Compare Failure |
GO to Pinpoint Test L |
Symptom Chart(s)
Symptom Chart: Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control
Diagnostics in this manual assume a certain skill level and knowledge of Ford-specific diagnostic practices.
REFER to: Diagnostic Methods (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
Symptom Chart
| Condition | Possible Sources | Actions |
| A module does not respond to the scan tool |
Fuse
Wiring, ABS SASM |
REFER to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| The brake warning indicator is always or never on |
Low brake fluid level Brake fluid level sensor Parking brake applied Parking brake switch Brake booster vacuum sensor IPC concern ABS concern |
RETRIEVE and DIAGNOSE all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). If there are no ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), DIAGNOSE the brake warning indicator. REFER to: Instrumentation, Message Center and Warning Chimes (413-01 Instrumentation, Message Center and Warning Chimes, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| The ABS warning indicator is always or never on |
IPC concern ABS concern SASM concern |
RETRIEVE and DIAGNOSE all ABS module and SASM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). If there are no ABS module or SASM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), DIAGNOSE the ABS warning indicator. REFER to: Instrumentation, Message Center and Warning Chimes (413-01 Instrumentation, Message Center and Warning Chimes, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| The stability/traction control OFF indicator (sliding-car OFF icon) is always on |
IPC concern ABS concern SASM concern |
RETRIEVE and DIAGNOSE all ABS module and SASM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). If there are no ABS module or SASM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), DIAGNOSE the ABS warning indicator. REFER to: Instrumentation, Message Center and Warning Chimes (413-01 Instrumentation, Message Center and Warning Chimes, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| ABS false activation, ABS too sensitive, ABS activates on normal stop |
Front or rear suspension concern |
ELIMINATE the front or rear suspension as the cause of the problem. REFER to: Suspension System (204-00 Suspension System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). |
| RCM mounting | CONFIRM the RCM is mounted correctly. REINSTALL as necessary. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). |
|
| Loose wheel speed sensor or excessive air gap |
INSPECT wheel speed sensor for looseness or excessive air gap. TIGHTEN or INSTALL new as necessary. For front wheel speed sensors, REFER to: Front Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 AntiLock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). For rear wheel speed sensors, REFER to: Rear Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
|
| Parking brake shoes out of adjustment (dragging) |
CHECK and if necessary, ADJUST the parking brake shoes. For vehicles equipped with rear drum brakes, REFER to: Parking Brake Cable Adjustment – Vehicles With: Rear Drum Brakes (206-05 Parking Brake and Actuation, General Procedures). For vehicles equipped with rear disc brakes, REFER to: Parking Brake Cable Adjustment – Vehicles With: Rear Disc Brakes (206-05 Parking Brake and Actuation, General Procedures). |
|
| The traction control system cannot be disabled — vehicles equipped with a 2.0L Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) engine |
Refer to the Diagnostic Routine |
GO to Pinpoint Test E |
| The traction control system cannot be disabled — vehicles equipped with a 2.0L Gasoline Turbocharged Direct Injection (GTDI) engine |
Refer to the Diagnostic Routine |
GO to Pinpoint Test S |
Diagnostic Routines
U3003:16
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42 for schematic and connector information.
The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) module, hydraulic pump and solenoid valves require an operating voltage that is
between 10 and 17 volts. The ABS module receives this voltage from the BJB. The ABS module has a single ground
circuit located in the engine compartment wiring harness. Excessive resistance or an open in one or more of these
circuits, a discharged battery or a inoperative charging system results in the ABS module setting a DTC.
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| U3003:16 | Battery Voltage: Circuit Voltage Below Threshold |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if the voltage supplied to the ABS module falls below 10 volts. |
Possible Causes
- Fuses
- Wiring, terminals or connectors
- ABS module
Visual Inspection and Diagnostic Pre-checks
- Make sure the vehicle battery terminals and cables are free of any corrosion and other contaminants.
- Make sure the vehicle battery terminals are tightened to their correct torque specifications.
- Make sure BJB fuses 7 (40A), 8 (30A) and 19 (5A) are OK.
PINPOINT TEST A : U3003:16
| A1 RECHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) |
Using a diagnostic scan tool, clear the ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Ignition OFF.
Ignition ON.
Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
Is DTC U3003:16 still present?
Yes GO to A2
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The DTC may have set due to a previous low battery voltage condition. |
A2 CHECK FOR CHARGING SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) IN THE PCM (POWERTRAIN
CONTROL MODULE)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, retrieve all Continuous Memory Diagnostic Trouble Codes (CMDTCs).
Is DTC B1317, B1318, B1676, U3003:16 or U3003:17 present in one or more modules AND are any charging
system Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the PCM?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE the charging system. REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L EcoBoost (184kW/250PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). |
No GO to A3
A3 CHECK THE BATTERY CONDITION AND STATE OF CHARGE
- Carry out the Battery Condition Test diagnostic routine.
REFER to: Battery (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, Diagnosis and Testing).
Did the battery pass the condition test?
| Yes | If the battery passed the condition test but required a recharge, DIAGNOSE the charging system. REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L EcoBoost (184kW/250PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). If the battery passed the condition test and did not require a recharge, GO to A4 |
| No | INSTALL a new battery. REFER to: Battery (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, Removal and Installation). |
A4 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE VOLTAGE (VPWR_ABS) PARAMETER
IDENTIFICATION (PID)
- Ignition ON.
- Measure and record the voltage at the battery.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, monitor the VPWR_ABS Parameter Identification (PID).
Is the Parameter Identification (PID) display within 0.2 volt of the recorded battery voltage?
Yes GO to A7
No GO to A5
A5 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE VOLTAGE SUPPLY
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect ABS module C135.
- Ignition ON.
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-1 | Ground | |
| C135-8 | Ground | |
| C135-32 | Ground |
Is each voltage within 0.2 volt of the recorded battery voltage?
Yes GO to A6
| No | VERIFY BJB fuses 7 (40A), 8 (30A) and 19 (5A) are OK. If not OK, REFER to the Wiring Diagrams manual to identify the cause of the circuit short. If OK, REPAIR the affected circuit for high resistance or an open. |
- A6 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE GROUND CIRCUIT FOR AN OPENIgnition OFF.
- Disconnect the battery negative cable.
- REFER to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-47 | Ground |
Is the resistance less than 3 ohms?
Yes GO to A7
No REPAIR the circuit.
- A7 CHECK FOR CORRECT ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OPERATIONIgnition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect ABS module C135 (if not previously disconnected).
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect ABS module C135. Make sure it seats and latches correctly.
- Connect the battery negative cable.
REFER to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures). - Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
Wheel Speed Sensor Erratic Signal Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
The wheel speed sensor uses the encoder (tone wheel) on the wheel bearing to generate a square wave signal
proportional to wheel speed that is sent to the ABS module. The wheel bearing, encoder and wheel speed sensor must
be undamaged and free from any contamination to produce a clean signal for use by the ABS module. Also, all 4 tires
and wheels must be of the same manufacturer recommended size for the wheel speed sensor to generate an accurate
wheel speed signal.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| C0030:07 | Left Front Tone Wheel: Mechanical Failure |
These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) set in continuous memory and on-demand if there is damage to the wheel speed sensor encoder, damage to the wheel bearing, or contamination or deformation of the wheel bearing seal. |
| C0033:07 | Right Front Tone Wheel: Mechanical Failure |
|
| C0036:07 | Left Rear Tone Wheel: Mechanical Failure |
|
| C0039:07 | Right Rear Tone Wheel: Mechanical Failure |
|
| C0031:07 | Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Mechanical Failure |
These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) set in continuous memory and on-demand if the wheel speed sensor, encoder and/or wheel bearing is damaged, or if the wheel bearing is not installed correctly. These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) also set if an incorrectly sized tire is installed on the vehicle or if an excessive air gap exists between the wheel speed sensor and the encoder due to an incorrect component being installed. |
| C0034:07 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Mechanical Failure |
|
| C0037:07 | Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Mechanical Failure |
|
| C003A:07 | Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Mechanical Failure |
PINPOINT TEST B : WHEEL SPEED SENSOR ERRATIC SIGNAL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
B1 CHECK FOR ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Retrieve and record all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Is DTC C0031:07, C0034:07, C0037:07 and/or C003A:07 present?
Yes GO to B2
| No | If DTCC0030:07, C0033:07, C0036:07 or C0039:07 is present, GO to B5 For all other ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), GO to the ABS Module DTC Chart. |
B2 CHECK THE TIRES SIZE AND PRESSURE
- Ignition OFF.
- Verify that all the tires and wheels are the same size and the tire size and inflation pressures are correct asindicated on the VC label.
Are the tires and wheels OK?
Yes GO to B3
No INSTALL the correct size tire/wheel or ADJUST tire pressure as necessary.
- B3 CHECK THE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR FOR DAMAGEWith the vehicle in NEUTRAL, position it on a hoist.
REFER to: Jacking and Lifting – Overview (100-02 Jacking and Lifting, Description and Operation). - Disconnect the suspect wheel speed sensor electrical connector.
- Inspect the wheel speed sensor and harness for abrasions, broken connector tabs or water intrusion.
Is the wheel speed sensor and harness OK?
Yes GO to B4
| No | INSTALL a new wheel speed sensor. For front wheel speed sensors, REFER to: Front Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). For rear wheel speed sensors, REFER to: Rear Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
B4 INSPECT THE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR MOUNTING
- Inspect the wheel speed sensor and fastener for looseness.
Are the wheel speed sensor and fastener tight?
Yes GO to B5
No TIGHTEN the wheel speed sensor fastener to specification.
B5 CHECK WHEEL BEARING AND ENCODER FOR DAMAGE
- Inspect the wheel bearings for abnormal wear or roughness and for deformation or contamination of the seal
and encoder.
Are the wheel bearing and encoder OK?
Yes GO to B6
| No | INSTALL a new wheel bearing as necessary. For the front wheel bearing, REFER to: Front Wheel Bearing (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation). For the rear wheel bearing, REFER to: Wheel Bearing and Wheel Hub (204-02 Rear Suspension, Removal and Installation). |
B6 CHECK FOR RETURNING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, clear all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Test drive the vehicle under normal driving conditions above 20 km/h (12 mph).
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
Are any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the ABS module?
| Yes | If Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) C0031:07, C0034:07, C0037:07 or C003A:07 is present, INSTALL a new wheel speed sensor. For front wheel speed sensors, REFER to: Front Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). For rear wheel speed sensors, REFER to: Rear Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). If Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) C0030:07, C0033:07, C0036:07 or C0039:07 is present, INSTALL a new wheel bearing as necessary. For the front wheel bearing, REFER to: Front Wheel Bearing (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation). For the rear wheel bearing, REFER to: Wheel Bearing and Wheel Hub (204-02 Rear Suspension, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
C0040:64
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 31 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
The ABS module receives brake pedal switch input from the PCM over the High Speed Controller Area Network (HSCAN). The ABS module compares this information against wheel speed sensor input to determine if the brake pedal input
is valid. As vehicle speed decreases, the ABS module looks for a change in the brake pedal switch input, if vehicle speed
decreases but there is no change in the brake pedal switch, the ABS sets a DTC. An incorrectly installed brake pedal
switch can cause a signal plausibility concern. Also, an implausible signal can been created if a driver is resting one foot
on the brake pedal while using the other foot to press the accelerator.
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| C0040:64 | Brake Pedal Switch “A”: Signal Plausibility Failure |
This DTC sets in continuous memory if brake pedal switch input is continuously active for more than 6 minutes when driving faster than 20 km/h (12 mph) or after accelerating up to a speed greater than 40 km/h (25 mph) and decelerating down to a speed less than 3 km/h (2 mph) 4 times with no change in brake pedal switch input. |
Possible Causes
- Brake pedal (stoplamp) switch
- Communication concern
- ABS module
Visual Inspection and Diagnostic Pre-checks
- Make sure the stoplamp switch electrical connector is connected and free of corrosion and other contaminants.
- Make sure the stoplamp switch is installed correctly.
- Make sure the stoplamp switch is operating correctly.
PINPOINT TEST C : C0040:64
C1 CHECK THE STOPLAMP SWITCH AND SPEED CONTROL DEACTIVATION SWITCH OPERATION
- Inspect the stoplamp switch (cruise control deactivation switch is part of the stoplamp switch) and brake pedal
assembly to verify there is no brake pedal pressure applied due to incorrect switch or pedal assembly
installation. - Confirm that all brake pedal bracket fasteners are tightened to specifications.
- Set the ignition to RUN.
- NOTE: Using the diagnostic scan tool recording function makes it easier to observe the brake pressure
sensor readings. - Using a diagnostic scan tool, monitor the Brake Switch Parameters.
- NOTE: The rate of brake pedal apply must not exceed 35 kPa (5.08 psi) per second as indicated by the
diagnostic scan tool.
Slowly apply the brake pedal to generate the pressure graph for the master cylinder pressure (MC_PRESS)
Parameter Identification (PID). - Record the initial value of the MC_PRESS Parameter Identification (PID) when the brake lamp
(BRAKE_LAMP) and cruise control cancel (CRUISE_CANCL) Parameter Identifications (PIDs) change from
OFF to ON.
Do the BRAKE_LAMP and CRUISE_CANCL Parameter Identifications (PIDs) transition to ON before the
MC_PRESS Parameter Identification (PID) reaches 304 kPa (44.09 psi)?
Yes GO to C2
| No | REMOVE and REINSTALL the stoplamp switch. REFER to: Stoplamp Switch (417-01 Exterior Lighting, Removal and Installation). CLEAR the ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). VERIFY if the concern is still present using the diagnostic scan tool as instructed previously. If the concern is still present, INSTALL a new stoplamp switch. REFER to: Stoplamp Switch (417-01 Exterior Lighting, Removal and Installation). If the concern is no longer present, the concern was most likely cause by an incorrectly installed stoplamp switch. |
C2 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Retrieve and record all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Are any communication (U-code) Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the ABS module?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE all ABS module communication Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) before diagnosing DTC C0040:64. GO to the ABS Module DTC Chart. |
No GO to C3
C3 CHECK THE PCM (POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE) FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the PCM KOEO self-test.
- Retrieve and record all PCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Are any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the PCM?
| Yes | REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4, Diagnosis and Testing). |
No GO to C4
C4 CHECK FOR CORRECT ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OPERATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect ABS module C135.
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect ABS module C135. Make sure it seats and latches correctly.
- Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
U0140:00
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
With the ignition ON, the BCM sends messages to the ABS module and the SASM over the High Speed Controller Area
Network (HS-CAN). If the ABS module or the SASM do not receive these messages within the specified time frame, the
modules set Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). This can be due to a BCM failure, a circuit failure on the High Speed
Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) or an excessive load on the network. For information on the messages sent to the
ABS module and the SASM by the BCM,
REFER to: Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – System Operation and Component Description (206-09
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Description and Operation).
1/23/2021 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – Diagnosis and Testing • 2012 Ford Focus •
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| U0140:00 | Lost Communication With Body Control Module: No Sub Type Information |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand in the ABS module if any of the following messages is missing from the BCM; odometer value, parking brake status, vehicle mode or vehicle configuration information. This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand in the SASM if the module does not receive the power mode or vehicle configuration information messages. |
Possible Causes
- Wiring, terminals or connectors
- Over or undervoltage concerns
- BCM
- ABS module
- SASM
PINPOINT TEST D : U0140:00
D1 CHECK THE COMMUNICATION NETWORK
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the Network Test.
Does the BCM pass the Network Test?
Yes GO to D2
| No | To diagnose the BCM does not communicate with the diagnostic scan tool, REFER to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Diagnosis and Testing). |
D2 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OR SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR
MODULE) CONTINUOUS MEMORY DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (CMDTCS)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test or the SASM self-test.
- Retrieve and record all ABS module or SASM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Repeat the ABS module or SASM self-test.
Is DTC U0140:00 retrieved again?
Yes GO to D3
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The DTC may have been set due to high network traffic or an intermittent fault condition. |
D3 CHECK FOR VOLTAGE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) FROM THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKESYSTEM) MODULE OR SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE) SELF-TEST
- Review the recorded Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from the ABS module or SASM self-test.
Is DTC U3003:16 or U3003:17 present in the ABS module or DTC U3003:62 present in the SASM ?
| Yes | For ABS module DTC U3003:16, GO to Pinpoint Test A For ABS module DTC U3003:17, GO to Pinpoint Test F For SASM DTC U3003:62, GO to Pinpoint Test L |
No GO to D4
D4 RETRIEVE ALL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) FROM THE BCM (BODY CONTROL MODULE)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the BCM self-test.
- Retrieve and record all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from the BCM self-test.
Is DTC U3003:16 or U3003:17 present in the BCM?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE the BCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REFER to: Body Control Module (BCM) (419-10 Multifunction Electronic Modules, Diagnosis and Testing). |
No GO to D5
D5 CHECK FOR DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE) U0140:00 SET IN OTHER MODULES
- Using the diagnostic scan tool, carry out the self-test for all modules.
- Retrieve and record the Continuous Memory Diagnostic Trouble Codes (CMDTCs) from all modules.
Is DTC U0140:00 set in 2 or more modules other than the ABS module or SASM?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new BCM. REFER to: Body Control Module (BCM) (419-10 Multifunction Electronic Modules, Removal and Installation). |
| No | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
The Traction Control System Cannot Be Disabled — Vehicles Equipped With a 2.0L Gasoline Direct Injection
(GDI) Engine
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 60 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
When the driver deactivates traction control using the message center, the IPC sends a message to the BCM over the
Medium Speed Controller Area Network (MS-CAN) to disable traction control. The BCM, acting as a gateway, relays this
message to the ABS module over the High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN). The ABS module continues to
monitor for excessive wheel spin, but no longer takes any action when a traction event is detected.
After receiving the message from the BCM, the ABS module sends a message to the BCM over the High Speed
Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) to illuminate the stability/traction control disabled indicator (sliding car OFF icon). The
BCM, acting as a gateway, relays this message to the IPC over the Medium Speed Controller Area Network (MS-CAN).
The IPC responds by illuminating the stability/traction control disabled indicator (sliding car OFF icon). Traction control
remains deactivated until the driver changes the traction control state in the message center or until the ignition is cycled.
If equipped, MyKey® allows users to configure traction control to be either always on or selectable. If a MyKey®
restricted key is in use with the MyKey® traction control feature configured to “always on”, traction control cannot be
disabled. An admin key must be used to enable and disable traction control.
NOTE: For vehicles equipped with Intelligent Access (IA), this test requires the use of at least 2 Intelligent Access (IA)
keys programmed to the vehicle, one admin Intelligent Access (IA) key and one restricted Intelligent Access (IA) key.
NOTE: For vehicles not equipped with Intelligent Access (IA), this test requires the use of at least 2 Integrated Keyhead
Transmitters (IKTs) programmed to the vehicle, one admin Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT) and one restricted
Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT).
Possible Causes
- A MyKey® restricted key is in use
- Network communication concern
- IPC concern
- Message center concern
PINPOINT TEST E : THE TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM CANNOT BE DISABLED — VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH A 2.0L
GASOLINE DIRECT INJECTION (GDI) ENGINE
E1 VERIFY THAT THE KEY IN USE IS NOT RESTRICTED
- For vehicles equipped with Intelligent Access (IA),
- place 1 of the Intelligent Access (IA) keys inside the vehicle and all other Intelligent Access (IA) keys
at least 1 meter (3 feet) away from the vehicle. - press the start/stop button without pressing the brake pedal.
- For vehicles not equipped with Intelligent Access (IA), turn the ignition to the ON position.
- Monitor the message center.
Does the message center display MYKEY ACTIVE DRIVE SAFELY?
| Yes | The current Intelligent Access (IA) key or Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT) is a restricted key and is operating correctly. REPEAT the test using different Intelligent Access (IA) keys or Integrated Keyhead Transmitters (IKTs) until the message center does not display MYKEY ACTIVE DRIVE SAFELY. GO to E2 No GO to E2 |
E2 VERIFY THE MYKEY® TRACTION CONTROL SETTING
- Using the message center, verify the MyKey® traction control setting. Refer to the Owner’s Literature for
instructions on setting the MyKey® functions.
Is the MyKey® traction control setting configured to “always on”?
Yes GO to E3
No GO to E4
E3 VERIFY TRACTION CONTROL FUNCTION CAN BE DISABLED USING THE ADMIN INTELLIGENT ACCESS
(IA) KEY OR THE ADMIN INTEGRATED KEYHEAD TRANSMITTER (IKT)
- Using the message center, verify traction control can be enabled and disabled using the admin Intelligent
Access (IA) key or the admin Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT). Refer to the Owner’s Literature for
instructions on enabling and disabling traction control.
Can traction control be enabled and disabled using the admin Intelligent Access (IA) key or the admin
Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT)?
| Yes | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by the use of a restricted Intelligent Access (IA) key or restricted Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT). INFORM the customer that traction control can only be disabled using an admin Intelligent Access (IA) key or an admin Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT) when the MyKey® traction control setting is configured to “always on”. |
No GO to E4
E4 CHECK FOR ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
Retrieve and record all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Are any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the ABS module?
Yes GO to the ABS Module DTC Chart.
No GO to E5
E5 CHECK FOR IPC (INSTRUMENT PANEL CLUSTER) DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the IPC self-test.
- Retrieve and record all IPC Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Are any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the IPC?
| Yes | REFER to: Instrumentation, Message Center and Warning Chimes (413-01 Instrumentation, Message Center and Warning Chimes, Diagnosis and Testing). |
No GO to E6
E6 CHECK FOR BCM (BODY CONTROL MODULE) DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the BCM self-test.
- Retrieve and record all BCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Are any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the BCM?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE the BCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REFER to: Body Control Module (BCM) (419-10 Multifunction Electronic Modules, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused due to high network traffic or an intermittent fault condition. |
U3003:17
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
The ABS module, hydraulic pump and solenoid valves require an operating voltage between 10 and 17 volts. The ABS
module receives this voltage from the BJB. The ABS module has a single ground circuit located in the engine
compartment wiring harness. An overcharging condition in the charging system results in the ABS module setting a DTC.
This DTC may also set in the ABS module due to battery charging or vehicle jump starting events.
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| U3003:17 | Battery Voltage: Circuit Voltage Above Threshold |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if the voltage supplied to the ABS module is above 17 volts |
Possible Causes
- Charging system concern
- ABS module
PINPOINT TEST F : U3003:17
F1 CHECK FOR HIGH VOLTAGE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) SET IN OTHER MODULES
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, retrieve and record all Continuous Memory Diagnostic Trouble Codes
(CMDTCs).
Is DTC B1317, B1318, B1676, U3003:16 or U3003:17 present in one or more modules AND are any charging
system Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the PCM?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE the PCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4, Diagnosis and Testing). |
No GO to F2
F2 CHECK THE BATTERY VOLTAGE
- Turn off all interior lights, exterior lights and accessories.
- Start and run the engine at approximately 1,500 Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) for 3 minutes while monitoring
the battery voltage.
Is the battery voltage between 13 and 15.2 volts ?
Yes GO to F3
| No | DIAGNOSE the overcharging condition. REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L EcoBoost (184kW/250PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). |
F3 RECHECK FOR DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE) U3003:17
- Turn the engine off.
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Clear the ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Repeat the ABS module self-test.
Is DTC U3003:17 still present?
Yes GO to F4
| No | The system is operating normally at this time. The DTC may have been set previously during battery charging or while jump starting the vehicle. |
F4 CHECK FOR CORRECT ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OPERATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect ABS module C135 (if not previously disconnected).
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect ABS module C135. Make sure it seats and latches correctly.
- Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
Stability Control Sensor Signal Failure DTCs
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
The RCM measures vehicle yaw rate, lateral acceleration and longitudinal acceleration and sends the information to the
ABS module over a private High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN). This private High Speed Controller Area
Network (HS-CAN) is used only for communication between the RCM and the ABS module. The yaw rate sensor, lateral
and longitudinal accelerometers are contained in the RCM. A failure of the private High Speed Controller Area Network
(HS-CAN), RCM or the internal sensors causes the ABS module to set one or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| C0061:28, C0062:28, C0063:28 |
Lateral Acceleration, Longitudinal Acceleration, Yaw Rate Sensor: Signal Bias Level Out of Range/Zero Adjustment Failure |
These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) set in continuous memory and on-demand if the sensor signal is greater than the programmed sensor maximum plausible signal. |
| C0061:2F, C0063:2F |
Lateral Acceleration, Yaw Rate Sensor: Signal Erratic |
These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) set in continuous memory and on-demand if the sensor signal is out of range when the vehicle is standing still. |
| C0061:64, C0062:64, C0063:64 |
Lateral Acceleration, Longitudinal Acceleration, Yaw Rate Sensor: Signal Plausibility Failure |
These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) set in continuous memory and on-demand if the sensor signal does not match the other stability sensor signals (steering angle, yaw rate, longitudinal acceleration or lateral acceleration). |
| U0028:88 | Vehicle Communication Bus “A”: Bus Off |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand due to a circuit failure in the private High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) between the ABS module and the RCM. |
| U0151:00 | Lost Communication With Restraints Control Module: No Sub Type Information |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if the expected RCM messages such as yaw rate sensor, lateral and longitudinal accelerometers are missing for more than 5 seconds. |
| U0452:86 | Invalid Data Received from Restraints Control Module: Signal Invalid |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if one or more of the stability sensors inside the RCM fails and the sensor signal provided does not match other stability control sensor input. |
Possible Causes
- Wiring, terminals or connectors
- RCM
- ABS module
PINPOINT TEST G : STABILITY CONTROL SENSOR SIGNAL FAILURE DTCS
G1 CHECK THE COMMUNICATION NETWORK
- Ignition ON.
- Using the diagnostic scan tool, carry out the Network Test.
Does the RCM pass the Network Test?
Yes GO to G2
| No | To diagnose the RCM does not communicate with the diagnostic scan tool, REFER to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Diagnosis and Testing). |
G2 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE CONTINUOUS MEMORY DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE CODES (CMDTCS)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Retrieve and record all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Repeat the ABS module self-test.
Is DTC U0151:00 retrieved again?
Yes GO to G3
| No | For Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) C0061:28, 2F, 64; C0062:28, 64; C0063:28, 2F, 64; U0028:88 or U0452:86, GO to G7 For all other ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), GO to the ABS Module DTC Chart. If no Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) return, the system is operating correctly at this time. The DTC may have been set due to high network traffic or an intermittent fault condition. |
G3 REVIEW THE RECORDED DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) FROM THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE
SYSTEM) MODULE SELF-TEST
- Review the recorded Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from the ABS module self-test.
Is DTC U3003:16 or U3003:17 present in the ABS module?
Yes For DTC U3003:16, GO to Pinpoint Test A
For DTC U3003:17, GO to Pinpoint Test F
No GO to G4
G4 RETRIEVE ANY DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) FROM THE RCM (RESTRAINTS CONTROL
MODULE)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the RCM self-test.
Is DTC U3003:16 or U3003:17 present in the RCM?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE the RCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), REFER to: Airbag Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) – Vehicles With: First and Second Row Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) With Driver Knee Airbag (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Diagnosis and Testing). |
No GO to G5
G5 CHECK FOR DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE) U0151:00 SET IN OTHER MODULES
- Using the diagnostic scan tool, carry out the self-test for all modules.
- Retrieve and record the Continuous Memory Diagnostic Trouble Codes (CMDTCs) from all modules.
Is DTC U0151:00 recorded in any other module?
Yes GO to G13
No GO to G6
G6 VERIFY THE RCM (RESTRAINTS CONTROL MODULE) PART NUMBER
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, retrieve and record the RCM part number from the log viewer.
- Check the part number recorded against the number listed in the parts catalog or equivalent.
Does the part number on the RCM match the part number listed in the parts catalog or equivalent?
Yes GO to G7
| No | INSTALL the correct RCM. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). |
G7 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE IVD INITIALIZATION
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module IVD Initialization.
Does the ABS module IVD Initialization complete successfully?
Yes GO to G8
No GO to G9
G8 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
Are any stability control sensor Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), including no communication, invalid data
and bus off Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the ABS module?
Yes GO to G9
| No | The condition that set the DTC is not present at this time. The concern may have been caused due to a failed or an incomplete initialization. |
G9 CHECK THE PRIVATE HIGH SPEED CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (HS-CAN) CIRCUITS FOR A SHORT
TO VOLTAGE
- Depower the SRS.
REFER to: Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) Depowering and Repowering (501-20B Supplemental - Restraint System, General Procedures).
- Disconnect both RCM electrical connectors.
- Disconnect ABS module C135.
- Ignition ON.
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-18 | Ground | |
| C135-19 | Ground |
Is any voltage present?
Yes REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
No GO to G10
G10 CHECK THE PRIVATE HIGH SPEED CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (HS-CAN) CIRCUITS FOR A SHORT
TO GROUND
- Ignition OFF.
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-18 | Ground | |
| C135-19 | Ground |
Are the resistances greater than 10,000 ohms?
Yes GO to G11
No REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
G11 CHECK THE PRIVATE HIGH SPEED CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (HS-CAN) CIRCUITS FOR A SHORT
TOGETHER
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-18 | C135-19 |
Is the resistance greater than 10,000 ohms?
Yes GO to G12
No REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
G12 CHECK THE PRIVATE HIGH SPEED CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (HS-CAN) CIRCUITS FOR AN OPEN
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-18 | C310B-32 | |
| C135-19 | C310B-31 |
Are the resistances less than 3 ohms?
Yes GO to G13
No REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
G13 CHECK FOR CORRECT RCM (RESTRAINTS CONTROL MODULE) OPERATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect the RCM electrical connectors (if not previously disconnected).
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect the RCM electrical connectors. Make sure they seat and latch correctly.
- Repower the SRS.
- REFER to: Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) Depowering and Repowering (501-20B Supplemental
- Restraint System, General Procedures).
- Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new RCM. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
C0020:01, C0020:1C, C0020:71
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
The ABS module uses an internal solid state switch to operate the hydraulic pump motor. The ABS module tests the
hydraulic pump motor by activating it for 30 milliseconds. While the pump motor is activated, the ABS module monitors
the voltage drop across the hydraulic pump motor. After 30 milliseconds have passed, the ABS module stops applying
voltage to the pump motor and monitors the voltage that the spinning hydraulic pump motor is generating and the voltage
drop across the hydraulic pump motor solid state switch. If the monitored voltages are not within the specifications, the
ABS module sets one or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| C0020:01 | ABS Pump Motor Control: General Electrical Failure |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if there is an ABS module voltage supply concern, a module ground concern, a shorted hydraulic pump motor or an internal failure of the ABS module. |
| C0020:1C | ABS Pump Motor Control: Circuit Voltage Out of Range |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if of the following conditions exist: the voltage supplied to the ABS module is less than 11 volts, there is an open or high resistance in the module voltage supply circuit or the module ground circuit, the voltage drop across the activated pump motor is greater than 7.3 volts, the voltage output of the deactivated pump motor is less than 6 volts, the voltage drop across the solid state switch is greater than 0.93 volt or there is an open or high resistance on the hydraulic pump motor circuit between the ABS module and the HCU. |
| C0020:71 | ABS Pump Motor Control: Actuator Stuck |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if the ABS module detects the hydraulic pump motor is not rotating when it is commanded to run. |
Possible Causes
- Fuse
- Wiring, terminals or connectors
- HCU
- ABS module
Visual Inspection and Diagnostic Pre-checks
- Make sure the vehicle battery terminals and cables are free of any corrosion and other contaminants.
- Make sure the vehicle battery terminals are tightened to their correct torque specifications.
- Make sure BJB fuse 7 (40A) and the fuse socket are OK.
PINPOINT TEST H : C0020:01, C0020:1C, C0020:71
H1 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Retrieve and record all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Is Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) C0020:71 present in the ABS module?
Yes GO to H2
| No | If only DTC C0020:1C is present, GO to H3 If both Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) C0020:1C and C0020:01 are present, GO to H3 If only DTC C0020:01 is present, GO to H6 For all other ABSmodule Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), GO to the ABS Module DTC Chart. |
H2 CHECK PUMP MOTOR OPERATION
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, activate the ABS pump motor (PMP_MTR) active command.
- Listen for the ABS pump motor noise.
Does the ABS pump motor run for approximately 2 seconds?
Yes GO to H3
No GO to H6
H3 CHECK FOR FAULT REPEATABILITY
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, clear the ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Test drive the vehicle at speeds greater than 20 km/h (12 mph).
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Retrieve and record all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Are any ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) retrieved?
| Yes | For Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) C0020:71, GO to H6 For Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) C0020:1C, GO to H4 For all other ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), GO to the ABS Module DTC Chart. |
| No | The concern that caused the DTC is not present at this time. DISCONNECT and INSPECT the ABS module electrical connector. CLEAN or REPAIR the connector as necessary. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
H4 CHECK THE PUMP MOTOR VOLTAGE SUPPLY TO THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect ABS module C135.
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-1 | Ground |
Is the voltage greater than 11 volts?
Yes GO to H5
| No | VERIFY that BJB fuse 7 (40A) is OK. If OK, REPAIR the circuit. If not OK, REFER to the Wiring Diagrams manual to identify the cause of the circuit short. |
H5 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE GROUND CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect the battery negative cable.
- REFER to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-47 | Ground |
Is the resistance less than 3 ohms?
Yes GO to H6
No REPAIR the circuit.
H6 CHECK FOR CORRECT ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS) MODULE OPERATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect ABS module C135 (if not previously disconnected).
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect ABS module C135. Make sure it seats and latches correctly.
- Connect the battery negative cable.REFER to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
- Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
C0040:87 or U0100:00
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
With the ignition ON, the PCM sends messages to the ABS module over the High Speed Controller Area Network (HSCAN). If the ABS module does not receive these messages within the specified time frame, the ABS module sets
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). This can be due to a PCM failure, a circuit failure on the High Speed Controller Area
Network (HS-CAN) or an excessive load on the network. For information on the messages sent to the ABS module by the
PCM,
REFER to: Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – System Operation and Component Description (206-09
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Description and Operation).
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| C0040:87 | Brake Pedal Switch “A”: Missing Message |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if the brake pedal position message is missing for more than 500 ms. This can be due to a PCM failure, a stoplamp switch failure, a circuit failure on the High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) or an excessive load on the network. |
| U0100:00 | Lost Communication With ECM/PCM “A”: No Sub Type Information |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if any one of the following messages is missing; accelerator pedal position, cruise control status, power pack status or reverse gear. This can be due to a PCM failure, a circuit failure on the High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) or an excessive load on the network. |
Possible Causes
- Wiring, terminals or connectors
- PCM
- ABS module
PINPOINT TEST I : C0040:87 OR U0100:00
I1 CHECK THE COMMUNICATION NETWORK
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the Network Test.
Does the PCM pass the Network Test?
Yes GO to I2
| No | To diagnose the PCM does not communicate with the diagnostic scan tool, REFER to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Diagnosis and Testing). |
I2 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) CONTINUOUS MEMORY DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(CMDTCS)
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Clear the ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Retrieve and record the ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Is DTC C0040:87 or U0100:00 retrieved again?
Yes GO to I3
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The DTC may have been set due to high network traffic or an intermittent fault condition. |
I3 RETRIEVE THE RECORDED DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) FROM THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE
SYSTEM) SELF-TEST
- Check the recorded Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from the ABS self-test.
Is Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) U3003:16 or U3003:17 recorded?
Yes For DTC U3003:16, GO to Pinpoint Test A
For DTC U3003:17, GO to Pinpoint Test F
No GO to I4
I4 RETRIEVE THE RECORDED DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) FROM THE PCM (POWERTRAIN
CONTROL MODULE) SELF-TEST
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the PCM KOEO self-test.
Is DTC P0562 or P0563 present?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE the PCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4, Diagnosis and Testing). |
No GO to I5
I5 CHECK FOR DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE) U0100:00 SET IN OTHER MODULES
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the self-test for all modules.
- Retrieve the Continuous Memory Diagnostic Trouble Codes (CMDTCs) from all modules.
Is DTC U0100:00 set in 1 or more modules in addition to the ABS module?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new PCM. REFER to: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4, Removal and Installation). |
| No | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
U0101:00
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
With the ignition ON, the TCM sends messages to the ABS module over the High Speed Controller Area Network (HSCAN). If the ABS module does not receive these messages within the specified time frame, the ABS module sets
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). This can be due to a TCM failure, a circuit failure on the High Speed Controller Area
Network (HS-CAN) or an excessive load on the network. For information on the messages sent to the ABS module by the
TCM,
REFER to: Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – System Operation and Component Description (206-09
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Description and Operation).
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| U0101:00 | Lost Communication With TCM: No Sub Type Information |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if the selector lever (PRNDL) status message is missing. |
Possible Causes
- Wiring, terminals or connectors
- TCM
- ABS module
PINPOINT TEST J : U0101:00
J1 CHECK THE COMMUNICATION NETWORK
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the Network Test.
Does the TCM pass the Network Test?
Yes GO to J2
| No | To DIAGNOSE the TCM does not communicate with the diagnostic scan tool, REFER to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Diagnosis and Testing). |
J2 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) CONTINUOUS MEMORY DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(CMDTCS)
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Clear the ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Retrieve and record the ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Is DTC U0101:00 retrieved again?
Yes GO to J3
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The DTC may have been set due to high network traffic or an intermittent fault condition |
J3 REVIEW THE RECORDED DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) FROM THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE
SYSTEM) MODULE SELF-TEST
- Review the recorded Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from the ABS module self-test.
Is DTC U3003:16 or U3003:17 present in the ABS module?
Yes For DTC U3003:16, GO to Pinpoint Test A
For DTC U3003:17, GO to Pinpoint Test F
No GO to J4
J4 RETRIEVE THE RECORDED DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) FROM THE TCM (TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE) SELF-TEST
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the TCM self-test.
Is DTC P0702, P0882, P0883 or P1397 present?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE the TCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), REFER to: Automatic Transmission (307-01 Automatic Transmission – Vehicles With: 6-Speed PowerShift Transmission – DPS6/6DCT250) |
No GO to J5
J5 CHECK FOR DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE) U0101:00 SET IN OTHER MODULES
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the self-test for all modules.
- Retrieve the Continuous Memory Diagnostic Trouble Codes (CMDTCs) from all modules.
Is DTC U0101:00 present in 1 or more modules in addition to the ABS module?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new PCM, the TCM is part of the PCM. REFER to: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4, Removal and Installation). |
| No | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
U0126:00
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
With the ignition ON, the SASM sends messages to the ABS module over the High Speed Controller Area Network (HSCAN). If the ABS module does not receive these messages within the specified time frame, the ABS module sets
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). This can be due to a steering angle sensor failure, a circuit failure on the High Speed
Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) or an excessive load on the network. For information on the messages sent to the
ABS module by the SASM,
REFER to: Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – System Operation and Component Description (206-09
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Description and Operation).
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| U0126:00 | Lost Communication With Steering Angle Sensor Module: No Sub Type Information |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if either the steering angle count or the steering angle status messages is missing. |
Possible Causes
- Wiring, terminals or connectors
- SASM
- ABS module
PINPOINT TEST K : U0126:00
K1 CHECK THE COMMUNICATION NETWORK
I
- ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the Network Test.
Does the SASM pass the Network Test?
Yes GO to K2
| No | To DIAGNOSE the SASM does not communicate with the diagnostic scan tool, REFER to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Diagnosis and Testing). |
K2 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) CONTINUOUS MEMORY DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(CMDTCS)
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Clear the ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Retrieve and record the ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Is DTC U0126:00 retrieved again?
Yes GO to K3
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The DTC may have been set due to high network traffic or an intermittent fault condition. |
K3 REVIEW THE RECORDED DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) FROM THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE
SYSTEM) MODULE SELF-TEST
Review the recorded Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) from the ABS module self-test.
Is DTC U3003:16 or U3003:17 present in the ABS module?
Yes For DTC U3003:16, GO to Pinpoint Test A
For DTC U3003:17, GO to Pinpoint Test F
No GO to K4
K4 RETRIEVE THE RECORDED DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) FROM THE SASM (STEERING ANGLE
SENSOR MODULE) SELF-TEST
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the SASM self-test.
Is DTC U3003:62 present in the SASM?
Yes GO to Pinpoint Test L
No GO to K5
K5 CHECK FOR DTC (DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE) U0126:00 SET IN OTHER MODULES
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the self-test for all modules.
- Retrieve the Continuous Memory Diagnostic Trouble Codes (CMDTCs) from all modules.
Is DTC U0126:00 set in 1 or more modules in addition to the ABS module?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
| No | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
U3003:62 – SASM
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 31 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
The SASM receives battery voltage from the BCM and has a single ground circuit located in the instrument panel wiring
harness. Excessive resistance or an open in one or both of these circuits, a discharged battery, an inoperative charging
system or an overcharging condition in the charging system results in the SASM setting a DTC.
This DTC may also set in the SASM due to battery charging or vehicle jump starting events.
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| U3003:62 | Battery Voltage: Signal Compare Failure |
This DTC sets when the voltage received by the SASM falls below 6 volts or raises above 21 volts. |
Possible Causes
- Fuse
- Wiring, terminals or connectors
- Charging system concern
- SASM
- ABS module
Visual Inspection and Diagnostic Pre-checks
- Make sure the vehicle battery terminals and cables are free of any corrosion and other contaminants.
- Make sure the vehicle battery terminals are tightened to their correct torque specifications.
- Make sure BCM fuse 72 (7.5A) is OK.
PINPOINT TEST L : U3003:62 – SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE)
L1 CHECK FOR CHARGING SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS) IN THE PCM (POWERTRAIN
CONTROL MODULE)
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, retrieve ALL Continuous Memory Diagnostic Trouble Codes (CMDTCs).
Is DTC B1317, B1318, B1676, U3003:16 or U3003:17 present in one or more modules AND are any charging
system Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the PCM?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE the charging system. REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L EcoBoost (184kW/250PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). |
No GO to L2
L2 CHECK THE BATTERY CONDITION AND STATE OF CHARGE
- Ignition OFF.
- Carry out the Battery Condition Test diagnostic routine.
- REFER to: Battery (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, Diagnosis and Testing).
Did the battery pass the condition test?
| Yes | If the battery passed the condition test but required a recharge, DIAGNOSE the charging system. REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L EcoBoost (184kW/250PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). If the battery passed the condition test and did not require a recharge, GO to L3 |
| No | INSTALL a new battery. REFER to: Battery (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, Removal and Installation). |
L3 CHECK THE CHARGING SYSTEM VOLTAGE
NOTE: Do not allow the engine speed to increase above 2,000 Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) while performing this
step or the generator may self-excite and result in default charging system output voltage. If engine speed goes above
2,000 Revolutions Per Minute (RPM), turn the vehicle off and restart the engine before performing this step.
- Start the engine.
- Measure the voltage of the battery with and without a load on the charging system as follows:
- Turn off all accessories and run the engine at 1,500 Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) for a minimum of
2 minutes while measuring the battery voltage. - Turn on the headlights and the HVAC fan on high and run the engine at 1,500 Revolutions Per
Minute (RPM) for a minimum of 2 minutes while measuring the battery voltage.
Is the battery voltage between 13 and 15.2 volts?
Yes GO to L4
| No | DIAGNOSE the charging system. REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). REFER to: Charging System – 2.0L EcoBoost (184kW/250PS) – MI4 (414-00 Charging System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). |
L4 CHECK THE SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE) BATTERY VOLTAGE STATUS (VBATT_STATUS)
PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION (PID)
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Measure and record the voltage at the battery.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, monitor the SASM VBATT_Status Parameter Identification (PID).
Is the Parameter Identification (PID) display within 0.2 volt of the recorded battery voltage?
Yes GO to L7
No GO to L5
L5 CHECK THE VOLTAGE SUPPLY TO THE SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE)
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect SASM C226A.
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C226A-1 | Ground |
Is the voltage within 0.2 volt of the recorded battery voltage?
Yes GO to L6
| No | VERIFY BCM fuse 72 (7.2A) is OK. If OK, REPAIR the circuit. If not OK, REFER to the Wiring Diagrams manual to identify the cause of the circuit short. |
L6 CHECK THE SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE) GROUND CIRCUIT FOR AN OPEN
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C226A-14 | Ground |
Is the resistance less than 3 ohms?
Yes GO to L7
No REPAIR the circuit.
L7 CHECK FOR CORRECT SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE) OPERATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect all SASM electrical connectors.
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect the SASM electrical connectors. Make sure they seat and latch correctly.
- Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) Signal Failure DTCs
The SASM monitors steering wheel rotation speed, angle and direction of rotation and sends the information to the ABS
module over the High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN). A failure of the High Speed Controller Area Network
(HS-CAN), SASM or the internal sensors causes the ABS module to set one or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| C0051:28 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Signal Bias Level Out of Range/Zero Adjustment Failure |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if the absolute value of the measured steering wheel angle sensor is greater than 720 degrees or if the calculated steering angle offset is greater than 15 degrees. This is most likely caused by loose or worn steering or suspension components that result in a vehicle tracking or pull/drift issue. Also, an incorrectly installed SASM or clockspring may cause the steering angle to be offset. |
| C0051:54 | Steering Wheel Position Sensor: Missing Calibration |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if the steering angle status message “Not Initialized” is received by the ABS module for longer than 800 ms with vehicle speed above 15 km/h (9 mph). This is most likely caused by a new SASM that has not been calibrated, an undervoltage at the module or an internal failure of the module. |
| U0428:00 | Invalid Data Received from Steering Angle Sensor Module: No Sub Type Information |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if the steering angle status message sent by the SASM is “defective”. |
| U0428:2F | Invalid Data Received from Steering Angle Sensor Module: Signal Erratic |
The steering angle is measured in increments of 1 degree. This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if the steering angle sensor signal increases or decreases when it should remain stable. |
| U0428:61 | Invalid Data Received from Steering Angle Sensor Module: Signal Calculation Failure |
This DTC sets in continuous memory and on-demand if the calculated steering angle and the actual steering angle differ by more than 15 degrees. This is most likely caused by an incorrectly installed or damaged SASM but can also be caused by loose or worn steering or suspension components that result in excessive play in the steering system. |
| U0428:62 | Invalid Data Received from Steering Angle Sensor Module: Signal Compare Failure |
These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) set in continuous memory and on-demand if the steering angle sensor signal does not match other stability sensor signals (yaw rate, longitudinal acceleration, lateral acceleration, etc.). |
| U0428:64 | Invalid Data Received from Steering Angle Sensor Module: Signal Plausibility Failure |
|
| U0428:68 | Invalid Data Received from Steering Angle Sensor Module: Event Information |
PINPOINT TEST M : STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE (SASM) SIGNAL FAILURE DTCS
M1 CHECK FOR ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Retrieve and record all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Is DTC C0051:28 or C0051:54 present in the ABS module?
Yes GO to M2
| No | If Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) U0428:00, 61, 68 or 2F are present, GO to M4 If Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) U0428:62 or 64 are present, GO to M3 For all other ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), GO to the ABS Module DTC Chart. |
M2 VERIFY SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE) CALIBRATION
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the IVD Initialization procedure. Follow the diagnostic scan tool
directions. - Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Test drive the vehicle above 20 km/h (12 mph) and make at least 1 left turn and 1 right turn.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
Is DTC C0051:28 or C0051:54 present in the ABS module?
| Yes | INSPECT the front suspension, rear suspension, wheels and tires for a pulling condition. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to: Suspension System (204-00 Suspension System – General Information, Diagnosis and Testing). INSPECT the front suspension and the steering system for loose or worn components. REPAIR as necessary. For the front suspension, REFER to: Front Suspension – Overview (204-01 Front Suspension, Description and Operation). For the rear suspension, REFER to: Rear Suspension – Overview (204-02 Rear Suspension, Description and Operation). For the steering system, REFER to: Power Steering – System Operation and Component Description (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation). |
| No | The condition that caused the concern is no longer present. The concern was most likely due to an incomplete calibration or a failed calibration of the SASM. RETURN the vehicle to the customer. |
M3 CHECK THE SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE) PARAMETER IDENTIFICATIONS (PIDS)
- Park the vehicle with the wheels in the straight ahead position.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, monitor the SASM steering wheel angle (SW_ANGLE) Parameter Identification
(PID). - Starting from the center (straight ahead) position, turn the steering wheel to the right until it stops. Record the
SW_ANGLE Parameter Identification (PID) display. - Starting from the center (straight ahead) position, turn the steering wheel to the left until it stops. Record the
SW_ANGLE Parameter Identification (PID) display.
Does the Parameter Identification (PID) display at least 380 degrees after reaching each end of travel point?
Yes GO to M6
| No | CHECK the vehicle history and VERIFY if a new clockspring or SASM has been installed. If a new clockspring has been installed, VERIFY correct clockspring installation. REFER to: Clockspring (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). If a new SASM has been installed, GO to M4 If a new clockspring or SASM have not been installed, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
M4 INSPECT THE SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE) INSTALLATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Remove the clockspring.REFER to: Clockspring (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation).
- Inspect the SASM and the SASM electrical connector for any obvious signs of damage, corrosion, foreign
material or looseness.
Are the SASM and electrical connector OK?
Yes GO to M5
| No | REPAIR or INSTALL new as necessary. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
M5 VERIFY THE SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE) ZERO POSITION
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, monitor the SASM steering wheel angle (SW_ANGLE) Parameter Identification
(PID). - Turn the SASM rotor by hand until the SW_ANGLE displays 0 degrees.
- Ignition OFF.
- Install the clockspring.
REFER to: Clockspring (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). - Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, clear all Continuous Memory Diagnostic Trouble Codes (CMDTCs).
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
Are Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) U0428:00, 61, 68, 2F; U0428:62 or 64 present in the ABS module?
| Yes | INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The condition that caused the concern is no longer present. The concern was most likely due to an incorrectly installed SASM. RETURN the vehicle to the customer. For all other ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), GO to the ABS Module DTC Chart. |
M6 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE YAW RATE VALUE (YAW_RATE) PARAMETER
IDENTIFICATION (PID)
- Monitor the YAW_RATE Parameter Identification (PID).
Is the YAW_RATE Parameter Identification (PID) value between -0.05 and 0.05?
Yes GO to M7
No GO to M9
M7 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE LATERAL ACCELERATION (LAT_ACCL)
PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION (PID)
- Monitor the LAT_ACCL Parameter Identification (PID).
Is the LAT_ACCL Parameter Identification (PID) value between -0.4 and 0.4?
Yes GO to M8
No GO to M9
M8 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE LONGITUDINAL ACCELERATION (LNGACC)
PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION (PID)
- NOTE: The vehicle must be on level ground and at a complete standstill. Any vehicle movement results in
false values for this test. - Monitor the LNGACC Parameter Identification (PID).
Is the LNGACC Parameter Identification (PID) value between -0.4 and 0.4?
Yes GO to M10
No GO to M9
M9 CHECK THE RCM (RESTRAINTS CONTROL MODULE) INSTALLATION AND MOUNTING SURFACE
- Ignition OFF.
- Depower the SRS.REFER to: Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) Depowering and Repowering (501-20B Supplemental
Restraint System, General Procedures). - Inspect the RCM installation and make sure the fasteners are fully seated and tightened correctly.
REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and
Installation). - Inspect the RCM mounting surface for damage, corrosion or dirt.
Is the RCM installed correctly and is the mounting surface clean and free from damage?
Yes GO to M10
| No | REPAIR or INSTALL new as necessary. REFER to: Restraints Control Module (RCM) (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation). |
M10 CHECK FOR CORRECT SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE) OPERATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect all SASM electrical connectors (if not previously disconnected).
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect the SASM electrical connectors. Make sure it seats and latches correctly.
- Connect all RCM electrical connectors. Make sure they seat and latch correctly.
- Repower the Supplemental Restraint System (SRS).
REFER to: Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) Depowering and Repowering (501-20B Supplemental
Restraint System, General Procedures). - Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
C1A41:64
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 31 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
The ABS module receives CPP switch input from the PCM over the High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN). The
ABS module compares this information against brake pedal switch and sensor input to determine if the clutch pedal input
is valid. An incorrectly installed CPP switch can cause a signal plausibility concern. Also, an implausible signal can be
created if a driver is resting one foot on the clutch pedal while using the other foot to press the accelerator.
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| C1A41:64 | Clutch Pedal Switch “A”: Signal Plausibility Failure |
This DTC sets in continuous memory if the ABS module receives the brake pedal switch message but does not receive the clutch pedal switch message. |
Possible Causes
- CPP switch
- Communication concern
- PCM
- ABS module
Visual Inspection and Diagnostic Pre-checks
- Make sure the CPP switch electrical connector is connected and free of corrosion and other contaminants.
- Make sure the CPP switch is installed correctly.
- Make sure the CPP switch is operating correctly.
PINPOINT TEST N : C1A41:64
N1 CHECK THE PCM (POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE) CLUTCH PEDAL BEYOND TOP OF TRAVEL
SWITCH POINT (CPP_TOP) PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION (PID)
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, monitor the PCM CPP_TOP Parameter Identification (PID) while pressing and
releasing the clutch pedal.
Does the Parameter Identification (PID) display YES with the pedal pressed and NO with the pedal released?
Yes GO to N2
| No | DIAGNOSE the CPP switch. REFER to: Cruise Control (419-03 Cruise Control, Diagnosis and Testing). |
N2 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
- Retrieve and record all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Are any communication (U-code) Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the ABS module?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE all ABS module communication Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) before diagnosing DTC C1A41:64. GO to the ABS Module DTC Chart. |
No GO to N3
N3 CHECK THE PCM (POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE) FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the PCM KOEO self-test.
- Retrieve and record all PCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Are any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in the PCM?
Yes DIAGNOSE the PCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
REFER to: Electronic Engine Controls (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls – 2.0L Duratec-HE (125kW/170PS) –
MI4, Diagnosis and Testing).
No GO to N4
N4 CHECK FOR CORRECT ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OPERATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect ABS module C135.
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect ABS module C135. Make sure it seats and latches correctly.
- Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
Wheel Speed Sensor Electrical Fault DTCs – Front
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
Active wheel speed sensors generate a square wave signal proportional to wheel speed which is sent to the ABS
module. Each wheel speed sensor is connected to the ABS module through 2 wires and a connector at each wheel
speed sensor. One wire is for sensor voltage supply from the ABS module and the other wire is for the signal return to the
ABS module. When the ignition is set to RUN, the ABS module carries out a self-test by sending a reference voltage
through the wheel speed sensors and their circuitry.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| C0031:11 | Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Ground |
These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) set in continuous memory and on-demand if there is a short to ground in the sensor signal return circuit or if the sensor has an internal short to ground. |
| C0034:11 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Ground |
|
| C0031:15 | Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Battery or Open |
These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) set in continuous memory and on-demand if there is a short to battery voltage or an open in the sensor signal return circuit. A short to battery voltage may be due to the sensor signal return circuit and the sensor voltage supply circuit shorted together. These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) also set if the sensor has an internal short to battery voltage or an open circuit. |
| C0034:15 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Battery or Open |
Possible Causes
- Wiring, terminals or connectors
- Wheel speed sensor
- ABS module
Visual Inspection and Diagnostic Pre-checks
- Make sure the wheel speed sensor harness is routed correctly and is undamaged.
- Make sure the wheel speed sensor electrical connector is free from any corrosion or other contaminants.
PINPOINT TEST O : WHEEL SPEED SENSOR ELECTRICAL FAULT DTCS – FRONT
O1 CHECK FOR FAULT REPEATABILITY
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, clear all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Test drive the vehicle above 20 km/h (12 mph).
- Bring the vehicle to a safe stop.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
Is Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) C0031:11, C0031:15, C0034:11 and/or C0034:15 present?
| Yes | If the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester is available, GO to O2 If the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester is not available and DTC C0031:15 or C0034:15 is present, GO to O5 If the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester is not available and DTC C0031:11 or C0034:11 is present, GO to O7 |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. INSPECT both front wheel speed sensor electrical connectors and the ABS module electrical connector. REPAIR or CLEAN the connector as necessary. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
O2 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OUTPUT USING THE ROTUNDA ACTIVE WHEEL
SPEED SENSOR TESTER
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect the suspect wheel speed sensor electrical connector.
- Connect the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester to the wheel speed sensor connectors.
- Ignition ON.
- Select the correct system polarity on the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester and turn the powerswitch to the ON position.
Is the tester output LED illuminated?
Yes GO to O3
No GO to O5
O3 CHECK THE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR FOR A SHORT TO VOLTAGE WITH THE ROTUNDA ACTIVE WHEEL
SPEED SENSOR TESTER
- Observe the current overload LED on the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester.
Is the current overload LED illuminated?
Yes REPAIR the suspect wheel speed sensor circuit for a short to voltage.
No GO to O4
O4 CHECK THE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR OUTPUT WITH THE ROTUNDA ACTIVE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
TESTER
- Raise the suspect wheel until it can spin freely.
REFER to: Jacking and Lifting – Overview (100-02 Jacking and Lifting, Description and Operation). - While monitoring the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester, slowly spin the suspect wheel.
Do the sensor output Light-emitting Diodes (LEDs) illuminate and flash?
| Yes | The system is operating correctly at this time. INSPECT all wheel speed sensor electrical connectors and the ABS module electrical connectors. REPAIR or CLEAN the connector as necessary. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
| No | INSTALL a new wheel speed sensor. REFER to: Front Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
O5 CHECK THE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CIRCUITS FOR A SHORT TO BATTERY VOLTAGE
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect ABS module C135.
- Disconnect the suspect wheel speed sensor.
- Ignition ON.
- For the Left Front (LF) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-45 | Ground | |
| C135-46 | Ground |
For the Right Front (RF) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-33 | Ground | |
| C135-34 | Ground |
Is any voltage present?
Yes REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
No GO to O6
O6 CHECK THE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CIRCUITS FOR AN OPEN
- Ignition OFF.
- For the Left Front (LF) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-45 | C150-1 | |
| C135-46 | C150-2 |
For the Right Front (RF) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-33 | C160-2 | |
| C135-34 | C160-1 |
Are the resistances less than 3 ohms?
Yes GO to O7
No REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
O7 CHECK FOR SHORTED WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CIRCUITS
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect ABS module C135 (if not previously disconnected).
- Disconnect the suspect wheel speed sensor (if not previously disconnected).
- For the Left Front (LF) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C150-1 | C150-2 | |
For the Right Front (RF) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C160-1 | C160-2 |
Is the resistance greater 10,000 ohms?
Yes If DTC C0031:11 or C0034:11 are present, GO to O8
If DTC C0031:15 or C0034:15 are present, GO to O9
No REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
O8 CHECK THE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CIRCUITS FOR A SHORT TO GROUND
- For the Left Front (LF) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-45 | Ground | |
| C135-46 | Ground |
For the Right Front (RF) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-33 | Ground | |
| C135-34 | Ground |
Are the resistances greater than 10,000 ohms?
Yes GO to O9
No REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
O9 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OUTPUT
- Ignition OFF.
- Connect ABS module C135.
- Ignition ON.
- For the Left Front (LF) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C150-1 | C150-2 |
For the Right Front (RF) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C160-1 | C160-2 |
Is the voltage greater 10 volts?
| Yes | INSTALL a new wheel speed sensor. REFER to: Front Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
No GO to O10
O10 CHECK FOR CORRECT ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OPERATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect ABS module C135 (if not previously disconnected).
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect ABS module C135. Make sure it seats and latches correctly.
- Connect the suspect wheel speed sensor.
- Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
Wheel Speed Sensor Electrical Fault DTCs – Rear
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
Active wheel speed sensors generate a square wave signal proportional to wheel speed which is sent to the ABS
module. Each wheel speed sensor is connected to the ABS module through 2 wires and a connector at each wheel
speed sensor. One wire is for sensor voltage supply from the ABS module and the other wire is for the signal return to the
ABS module. When the ignition is set to RUN, the ABS module carries out a self-test by sending a reference voltage
through the wheel speed sensors and their circuitry.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| C0037:11 | Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Ground |
These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) set in continuous memory and on-demand if there is a short to ground in the sensor signal return circuit or if the sensor has an internal short to ground. |
| C003A:11 | Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Ground |
|
| C0037:15 | Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Battery or Open |
These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) set in continuous memory and on-demand if there is a short to battery voltage or an open in the sensor signal return circuit. A short to battery voltage may be due to the sensor signal return circuit and the sensor voltage supply circuit shorted together. These Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) also set if the sensor has an internal short to battery voltage or an open circuit. |
| C003A:15 | Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor: Circuit Short to Battery or Open |
Possible Causes
- Wiring, terminals or connectors
- Wheel speed sensor
- ABS module
Visual Inspection and Diagnostic Pre-checks
- Make sure the wheel speed sensor harness is routed correctly and is undamaged.
- Make sure the wheel speed sensor electrical connector is free from any corrosion or other contaminants.
PINPOINT TEST P : WHEEL SPEED SENSOR ELECTRICAL FAULT DTCS – REAR
P1 CHECK FOR FAULT REPEATABILITY
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, clear all ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Test drive the vehicle above 20 km/h (12 mph).
- Bring the vehicle to a safe stop.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
Is DTC C0031:11, C0031:15, C0034:11 and/or C0034:15 present?
| Yes | If the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester is available, GO to P2 If the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester is not available and DTC C0037:15 or C003A:15 is present, GO to P5 If the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester is not available and DTC C0037:11 or C003A:11 is present, GO to P7 |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. INSPECT both front wheel speed sensor electrical connectors and the ABS module electrical connector. REPAIR or CLEAN the connector as necessary. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
P2 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OUTPUT USING THE ROTUNDA ACTIVE WHEEL
SPEED SENSOR TESTER
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect the suspect wheel speed sensor electrical connector.
- Connect the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester to the wheel speed sensor connectors.
- Ignition ON.
- Select the correct system polarity on the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester and turn the power
switch to the ON position.
Is the tester output LED illuminated?
Yes GO to P3
No GO to P5
P3 CHECK THE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR FOR A SHORT TO VOLTAGE WITH THE ROTUNDA ACTIVE WHEEL
SPEED SENSOR TESTER
- Observe the current overload LED on the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester.
Is the current overload LED illuminated?
Yes REPAIR the suspect wheel speed sensor circuit for a short to voltage.
No GO to P4
P4 CHECK THE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR OUTPUT WITH THE ROTUNDA ACTIVE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
TESTER
- Raise the suspect wheel until it can spin freely.
REFER to: Jacking and Lifting – Overview (100-02 Jacking and Lifting, Description and Operation). - While monitoring the Rotunda Active Wheel Speed Sensor Tester, slowly spin the suspect wheel.
Do the sensor output Light-emitting Diodes (LEDs) illuminate and flash?
| Yes | The system is operating correctly at this time. INSPECT all wheel speed sensor electrical connectors and the ABS module electrical connectors. REPAIR or CLEAN the connector as necessary. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
| No | INSTALL a new wheel speed sensor. REFER to: Rear Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
P5 CHECK THE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CIRCUITS FOR A SHORT TO BATTERY VOLTAGE
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect ABS module C135.
- Disconnect the suspect wheel speed sensor.
- Ignition ON.
- For the Right Rear (RR) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-42 | Ground | |
| C135-43 | Ground |
Is any voltage present?
Yes REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
No GO to P6
P6 CHECK THE WHEEL SPEED CIRCUITS FOR AN OPEN
- Ignition OFF.
- For the Left Rear (LR) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-36 | C440-1 | |
| C135-37 | C440-2 |
For the Right Rear (RR) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-42 | C426-2 | |
| C135-43 | C426-1 |
Are the resistances less than 3 ohms?
Yes GO to P7
No REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
P7 CHECK FOR SHORTED WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CIRCUITS
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect ABS module C135 (if not previously disconnected).
- Disconnect the suspect wheel speed sensor (if not previously disconnected).
- For the Left Rear (LR) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C440-1 | C440-2 |
- For the Right Rear (RR) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C426-1 | C426-2 |
Is the resistance greater 10,000 ohms?
Yes If DTC C0037:11 or C003A:11 are present, GO to P8
If DTC C0037:15 or C003A:15 are present, GO to P9
No REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
P8 CHECK THE WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CIRCUITS FOR A SHORT TO GROUND
- For the Left Rear (LR) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-36 | Ground | |
| C135-37 | Ground |
- For the Right Rear (RR) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C135-42 | Ground | |
| C135-43 | Ground |
Are the resistances greater than 10,000 ohms?
Yes GO to P9
No REPAIR the affected circuit(s).
P9 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OUTPUT
- Ignition OFF.
- Connect ABS module C135.
- Ignition ON.
- For the Left Rear (LR) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C440-1 | C440-2 |
- For the Right Rear (RR) wheel speed sensor, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C426-1 | C426-2 |
Is the voltage greater 10 volts?
| Yes | INSTALL a new wheel speed sensor. REFER to: Rear Wheel Speed Sensor (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
No GO to P10
P10 CHECK FOR CORRECT ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OPERATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect ABS module C135 (if not previously disconnected).
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect ABS module C135. Make sure it seats and latches correctly.
- Connect the suspect wheel speed sensor.
- Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
U3003:62 – ABS Module
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
The ABS module, hydraulic pump and solenoid valves require an operating voltage that is between 10 and 17 volts. The
ABS module receives this voltage from the BJB. The BCM broadcasts a vehicle voltage message on the High Speed
Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) for other modules to use as a check for their own voltage inputs. Excessive resistance
or an open in the ABS module voltage circuits, a discharged battery, an inoperative charging system or a communication
concern results in the ABS module setting a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). This is most likely due to a concern in the
High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) or a concern in the vehicle battery or charging system.
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| U3003:62 | Battery Voltage: Signal Compare Failure |
This DTC sets when the vehicle voltage message sent from the BCM varies by more than 2 volts from the actual voltage measured by the ABS module. |
Possible Causes
- Fuse
- Wiring, terminals or connectors
- Communication concern
- Charging system concern
- Vehicle battery
- BCM
- ABS module
PINPOINT TEST Q : U3003:62 – ABS MODULE
Q1 CHECK FOR ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE BATTERY VOLTAGE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES (DTCS)
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
Is DTC U3003:16 or U3003:17 present?
Yes For DTC U3003:16 GO to Pinpoint Test A
For DTC U3003:17 GO to Pinpoint Test F
No GO to Q2
Q2 CHECK FOR ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE COMMUNICATION DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES (DTCS)
- Review the results of the previous ABS module self-test.
Is DTC U0140:00 present in the ABS module?
Yes GO to Pinpoint Test D
No GO to Q3
Q3 CHECK FOR BCM (BODY CONTROL MODULE) BATTERY VOLTAGE DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(DTCS)
Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the BCM self-test.
Is DTC U3003:16 and/or U3003:17 present in the BCM?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE the BCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). REFER to: Body Control Module (BCM) (419-10 Multifunction Electronic Modules, Diagnosis and Testing). |
No GO to Q4
Q4 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE VOLTAGE SUPPLY (VPWR_ABS) PARAMETER
IDENTIFICATION (PID) AND THE BCM (BODY CONTROL MODULE) BATTERY VOLTAGE (V_BATT) PARAMETER
IDENTIFICATION (PID)
- Measure and record the voltage at the battery.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, observe the ABS module VPWR_ABS and the BCM V_BATT Parameter
Identifications (PIDs).
Do both Parameter Identifications (PIDs) display within 0.2 volt of the recorded battery voltage?
| Yes | The condition that caused the DTC to set is not present at this time. The DTC may have been set due to excessive resistance at the battery terminals or in the High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN). INSPECT the battery terminals for dirt, corrosion and other foreign material that could cause excessive resistance. VERIFY the integrity of the module connectors and wiring. REPAIR as necessary. |
| No | If the ABS module VPWR_ABS Parameter Identification (PID) does not display within 0.2 volt of battery voltage, GO to Pinpoint Test A If the BCM V_BATT Parameter Identification (PID) does not display within 0.2 volt of battery voltage, DIAGNOSE the BCM. REFER to: Body Control Module (BCM) (419-10 Multifunction Electronic Modules, Removal and Installation). |
U0300:00
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 42 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
The ABS module and the SASM require correct vehicle configuration information to operate correctly. This information is
programmed into the module when a new module is installed. The BCM is also programmed with the vehicle
configuration information and shares this information with other modules over the High Speed Controller Area Network
(HS-CAN). Incomplete or improper flash programming procedures, a loss of communication between the BCM and ABS
module or SASM, swapping modules between vehicles or an internal failure of one or more modules causes a mismatch
of vehicle configuration information between the modules.
DTC Fault Trigger Conditions
| DTC | Description | Fault Trigger Conditions |
| U0300:00 | Internal Control Module Software Incompatibility: No Sub Type Information |
This DTC sets when the vehicle configuration information transmitted by the BCM does not match what is stored in the ABS module or the SASM. |
PINPOINT TEST R : U0300:00
R1 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OR SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR
MODULE) AND BCM (BODY CONTROL MODULE) DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTCS)
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module or SASM self-test.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the BCM self-test.
Are there any communication or module internal failure Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) present in either of
the modules?
| Yes | For ABS module Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), GO to the ABS Module DTC Chart. For SASM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), GO to the SASM DTC Chart. For BCM Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), REFER to: Body Control Module (BCM) (419-10 Multifunction Electronic Modules, Diagnosis and Testing). |
No If DTC U0300:00 is present in the ABS module, GO to R2
If DTC U0300:00 is present in the SASM, GO to R3
R2 PROGRAM THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, program the ABS module using as-built data.
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module self-test.
Is DTC U0300:00 present in the ABS module?
Yes GO to R4
No The concern was caused by an incomplete or improperly programmed ABS module, the repair is
complete.
R3 PROGRAM THE SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, program the SASM using as-built data.
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the SASM self-test.
Is DTC U0300:00 present in the SASM?
Yes GO to R4
No The concern was caused by an incomplete or improperly programmed SASM, the repair is
complete.
R4 PROGRAM THE BCM (BODY CONTROL MODULE)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, program the BCM using as-built data.
- Ignition OFF.
- Ignition ON.
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, carry out the ABS module or SASM self-test.
Is DTC U0300:00 present in the ABS module or SASM?
| Yes | If DTC U0300:00 is present in the ABS module, GO to R5 If DTC U0300:00 is present in the SASM, GO to R6 |
| No | The concern was caused by a incomplete or improperly programmed BCM, the repair is complete. |
R5 CHECK FOR CORRECT ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OPERATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect ABS module C135.
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect ABS module C135. Make sure it seats and latches correctly.
- Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
R6 CHECK FOR CORRECT SASM (STEERING ANGLE SENSOR MODULE) OPERATION
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect and inspect the SASM electrical connectors.
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect the SASM electrical connectors. Make sure they seat and latch correctly.
- Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new SASM. REFER to: Steering Angle Sensor Module (SASM) (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |
The Traction Control System Cannot Be Disabled — Vehicles Equipped With a 2.0L Gasoline Turbocharged
Direct Injection (GTDI) Engine
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Cell 60 for schematic and connector information.
Normal Operation and Fault Conditions
When the driver deactivates traction control or Electronic Stability Control (ESC) using the Electronic Stability Control
(ESC) OFF switch, the ABS module continues to monitor for vehicle instability and excessive wheel spin but no longer
takes any action when either condition is detected.
The Electronic Stability Control (ESC) OFF switch uses 2 circuits, one circuit is hardwired to the ABS module and the
other circuit is ground. When the switch is pressed, the ABS module detects the ground signal and sends a message to
the BCM over the High Speed Controller Area Network (HS-CAN) to illuminate the stability/traction control disabled
indicator (sliding car OFF icon). The BCM, acting as a gateway, relays this message to the IPC over the Medium Speed
1/23/2021 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control – Diagnosis and Testing • 2012 Ford Focus
Controller Area Network (MS-CAN). The IPC responds by illuminating the stability/traction control disabled indicator
(sliding car OFF icon).
A short to ground in the ABS module hardwired circuit, an open in one or both of the circuits, an inoperative switch or an
internal failure in the ABS module causes the traction control disable function to become inoperative.
If equipped, MyKey® allows users to configure traction control to be either always on or selectable. If a MyKey®
restricted key is in use with the MyKey® traction control feature configured to “always on”, traction control cannot be
disabled. An admin key must be used to enable and disable traction control.
NOTE: For vehicles equipped with Intelligent Access (IA), this test requires the use of at least 2 Intelligent Access (IA)
keys programmed to the vehicle, one admin Intelligent Access (IA) key and one restricted Intelligent Access (IA) key.
NOTE: For vehicles not equipped with Intelligent Access (IA), this test requires the use of at least 2 Integrated Keyhead
Transmitters (IKTs) programmed to the vehicle, one admin Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT) and one restricted
Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT).
PINPOINT TEST S : THE TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM CANNOT BE DISABLED — VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH A 2.0L
GASOLINE TURBOCHARGED DIRECT INJECTION (GTDI) ENGINE
S1 VERIFY THAT THE KEY IN USE IS NOT RESTRICTED
- For vehicles equipped with Intelligent Access (IA),
- place 1 Intelligent Access (IA) key inside the vehicle and all other Intelligent Access (IA) keys at
least 1 meter (3 feet) away from the vehicle. - press the start/stop button without pressing the brake pedal.
- For vehicles without Intelligent Access (IA), turn the ignition to the ON position.
- Monitor the message center.
Does the message center display MYKEY ACTIVE DRIVE SAFELY?
| Yes | The current Intelligent Access (IA) key or Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT) is a restricted key and is functioning correctly. REPEAT the test using different Intelligent Access (IA) keys or Integrated Keyhead Transmitters (IKTs) until the message center does not display MYKEY ACTIVE DRIVE SAFELY. GO to S2 |
No GO to S2
S2 VERIFY THE MYKEY® TRACTION CONTROL SETTING
- Using the message center, verify the MyKey® traction control setting configuration. Refer to the Owner’s
Literature for information on configuring the MyKey® functions.
Is the MyKey® traction control setting configured to “always on”?
Yes GO to S3
No GO to S4
S3 VERIFY TRACTION CONTROL FUNCTION CAN BE DISABLED USING THE ADMIN INTELLIGENT ACCESS
(IA) KEY OR INTEGRATED KEYHEAD TRANSMITTER (IKT)
- With the admin Intelligent Access (IA) key or Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT) in the vehicle or ignition,
press the Electronic Stability Control (ESC) OFF switch once.
Does the sliding car OFF icon illuminate and does the message center display TRACTION CONTROL OFF?
| Yes | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by the use of a restricted Intelligent Access (IA) key or Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT) with the MyKey® traction control setting configured to “always on”. INFORM the customer that traction control can only be disabled using an admin Intelligent Access (IA) key or Integrated Keyhead Transmitter (IKT) when the MyKey® traction control setting is configured to “always on”. |
No GO to S4
S4 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH STATUS
(TC_SW_STAT) PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION (PID)
- Using a diagnostic scan tool, view the ABS module TC_SW_STAT Parameter Identification (PID).
- Press and release the Electronic Stability Control (ESC) OFF switch while monitoring the ABS module
TC_SW_STAT Parameter Identification (PID).
Does the Parameter Identification (PID) display ON when the switch is pressed and OFF when the switch is
released?
Yes GO to S5
No GO to S6
S5 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM STATUS
(TC_SYS_STAT) PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION (PID)
- Press and release the Electronic Stability Control (ESC) OFF switch while monitoring the ABS module
TC_SYS_STAT Parameter Identification (PID).
Does the Parameter Identification (PID) display ON when the switch is pressed and OFF when the switch is
released?
| Yes | DIAGNOSE the stability/traction control disabled indicator (sliding car OFF icon) and message center. REFER to: Instrumentation, Message Center and Warning Chimes (413-01 Instrumentation, Message Center and Warning Chimes, Diagnosis and Testing). |
No GO to S6
S6 CHECK THE ELECTRONIC STABILITY CONTROL (ESC) OFF SWITCH
- Ignition OFF.
- Disconnect Electronic Stability Control (ESC) OFF switch C280.
- While pressing and releasing the Electronic Stability Control (ESC) OFF switch, measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C280-4Component Side | C280-12Component Side |
Is the resistance less than 3 ohms when the switch is pressed and greater than 10,000 ohms when the switch is
released?
Yes GO to S7
No INSTALL a new Electronic Stability Control (ESC) OFF switch.
S7 CHECK THE ELECTRONIC STABILITY CONTROL (ESC) OFF SWITCH CIRCUITS FOR AN OPEN
- Disconnect ABS module C135.
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C280-4 | C135-4 |
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C280-12 | Ground |
Are the resistances less than 3 ohms?
Yes GO to S8
No REPAIR the affected circuit.
S8 CHECK THE ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE HARDWIRED CIRCUIT FOR A SHORT TO
GROUND
- Measure:
| Positive Lead | Measurement / Action | Negative Lead |
| C280-4 | Ground |
Is the resistance greater than 10,000 ohms?
Yes GO to S9
No REPAIR the circuit.
S9 CHECK FOR CORRECT ABS (ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM) MODULE OPERATION
- Inspect ABS module C135.
- Repair:
- corrosion (install new connector or terminal – clean module pins)
- damaged or bent pins – install new terminals/pins
- pushed-out pins – install new pins as necessary
- Connect ABS module C135. Make sure it seats and latches correctly.
- Connect Electronic Stability Control (ESC) OFF switch C280.
- Operate the system and determine if the concern is still present.
Is the concern still present?
| Yes | CHECK OASIS for any applicable Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs). If a TSB exists for this concern, DISCONTINUE this test and FOLLOW the TSB instructions. If no Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) address this concern, INSTALL a new ABS module and HCU. REFER to: Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) (206-09 Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) and Stability Control, Removal and Installation). |
| No | The system is operating correctly at this time. The concern may have been caused by a loose or corroded connector. ADDRESS the root cause of any connector or pin issues. |